Page 83 - AIH-2-1
P. 83
Artificial Intelligence in Health ViT for Glioma Classification in MRI
A B
Figure 8. Comparison between three- and two-class classification problem. (A) Confusion matrix for a three-class problem with HGG, LGG, and
nontumor. (B) Confusion matrix for a two-class problem with tumor (HGG and LGG tumors) and nontumor.
Abbreviations: HGG: High-grade glioma; LGG: Low-grade glioma.
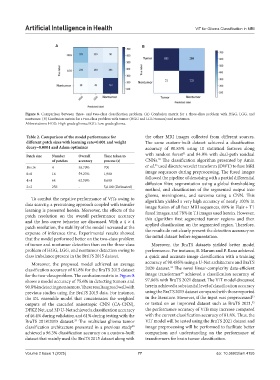
Table 2. Comparison of the model performance for the other MRI images collected from different sources.
different patch sizes with learning rate=0.001 and weight The same custom-built dataset achieved a classification
decay=0.0001 and Adam optimizer accuracy of 80.85% using 10 statistical features along
31
Patch size Number Overall Time taken to with random forest and 84.9% with dual-path residual
32
of patches accuracy process (s) CNNs. The classification algorithm presented by Amin
33
16×16 4 56.70% 700 et al. used discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to fuse MRI
8×8 16 59.23% 1,900 image sequences during preprocessing. The fused images
4×4 64 62.56% 8,600 followed the pipeline of denoising with a partial differential
diffusion filter, segmentation using a global thresholding
2×2 256 - 5,6100 (Estimated)
method, and classification of the segmented output into
glioma, meningioma, and sarcoma using a CNN. This
To combat the negative performance of ViTs owing to algorithm yielded a very high accuracy of nearly 100% in
data scarcity, a pretraining approach coupled with transfer image fusion of all four MRI sequences, 89% in Flair + T1
learning is presented herein. Moreover, the effects of the fused images, and 78% in T1 images used herein. However,
patch resolution on the overall performance accuracy this algorithm first segmented tumor regions and then
and the loss curve behavior are discussed. With a 4 × 4
patch resolution, the stability of the model increased at the applied classification on the segmented region. Therefore,
expense of inference time. Experimental results showed the results do not clearly present the detection accuracy on
that the model performed better on the two-class problem the initial dataset before segmentation.
of tumor and nontumor detection than on the three-class Moreover, the BraTS datasets yielded better model
problem of HGG, LGG, and nontumor detection owing to performance. For instance, B. Maram and P. Rana achieved
class imbalance present in the BraTS 2015 dataset. a quick and accurate image classification with a training
Moreover, the proposed model achieved an average accuracy of 98.485% using a U-Net architecture and BraTS
34
classification accuracy of 81.8% for the BraTS 2015 dataset 2020 dataset. The novel linear-complexity data-efficient
35
for the two-class problem. The confusion matrix in Figure 8 image transformer achieved a classification accuracy of
shows a model accuracy of 75.6% in detecting tumors and 97.86% with BraTS 2021 dataset. The ViT model discussed
90.8% in detecting nontumors. These results agreed well with herein achieved a substantial level of classification accuracy
previous studies using the BraTS 2015 data. For instance, using the BraTS 2015 dataset compared with those reported
33
the DL ensemble model that concatenates the weighted in the literature. However, if the input was preprocessed
35
outputs of the cascaded anisotropic CNN (CA-CNN), or tested on an improved dataset such as BraTS 2021,
DFKZ Net, and 3D U-Net achieved a classification accuracy the performance accuracy of ViTs may increase compared
of 46.4% during validation and 61% during testing with the with the current classification accuracy of 81.8%. Thus, the
BraTS 2018/2015 dataset. The multiclass glioma tumor ViT model will be tested using the BraTS 2021 dataset and
29
classification architecture presented in a previous study image preprocessing will be performed to facilitate better
30
achieved a 96.3% classification accuracy on a custom-built comparison and understanding on the performance of
dataset that mainly used the BraTS 2015 dataset along with transformers for brain tumor classification.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 77 doi: 10.36922/aih.4155