Page 81 - AIH-2-1
P. 81
Artificial Intelligence in Health ViT for Glioma Classification in MRI
A B
C
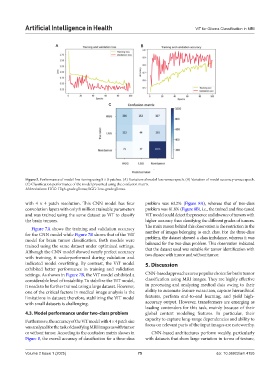
Figure 5. Performance of model fine-tuning using 8 × 8 patches. (A) Variation of model loss versus epoch. (B) Variation of model accuracy versus epoch.
(C) Classification performance of the model presented using the confusion matrix.
Abbreviations: HGG: High-grade glioma; LGG: Low-grade glioma.
with 4 × 4 patch resolution. This CNN model has four problem was 63.2% (Figure 8A), whereas that of two-class
convolution layers with only 8 million trainable parameters problem was 81.8% (Figure 8B), i.e., the trained and fine-tuned
and was trained using the same dataset as ViT to classify ViT model could detect the presence and absence of tumors with
the brain tumors. higher accuracy than classifying the different grades of tumors.
The main reason behind this observation is the restriction in the
Figure 7A shows the training and validation accuracy
for the CNN model while Figure 7B shows that of the ViT number of images belonging to each class. For the three-class
problem, the dataset showed a class imbalance, whereas it was
model for brain tumor classification. Both models were
trained using the same dataset under optimized settings. balanced for the two-class problem. This observation indicated
Although the CNN model showed nearly prefect accuracy that the dataset used was suitable for tumor identification with
with training, it underperformed during validation and two classes: with tumor and without tumor.
indicated model overfitting. By contrast, the ViT model 5. Discussion
exhibited better performance in training and validation
settings. As shown in Figure 7B, the ViT model exhibited a CNN-based approaches are a popular choice for brain tumor
considerable level of instability. To stabilize the ViT model, classification using MRI images. They are highly effective
it needs to be further trained using a large dataset. However, in processing and analyzing medical data owing to their
one of the critical factors in medical image analysis is the ability to automate feature extraction, capture hierarchical
limitations in dataset; therefore, stabilizing the ViT model features, perform end-to-end learning, and yield high-
with small datasets is challenging. accuracy output. However, transformers are emerging as
leading contenders for this task, mainly because of their
4.3. Model performance under two-class problem global context modeling features. In particular, their
Furthermore, the accuracy of the ViT model with 4 × 4 patch size capacity to capture long-range dependencies and ability to
was analyzed for the task of classifying MRI images as with tumor focus on relevant parts of the input images are noteworthy.
or without tumor. According to the confusion matrix shown in CNN-based architectures perform weakly, particularly
Figure 8, the overall accuracy of classification for a three-class with datasets that show large variation in terms of texture,
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 75 doi: 10.36922/aih.4155