Page 96 - AIH-2-1
P. 96
Artificial Intelligence in Health Benchmarking ML imputation in mental health surveys
and accurate. This shows that when a block of correlated
variables in one survey is completely missing, other related
surveys or medical history can also provide relevant
information for imputation. The choice of imputation
methods may depend on the overall missing rate and
missingness patterns in a dataset.
The strength of our study is that a large-scale collection
of mental and behavioral surveys in SPARK was utilized
to simulate the missingness patterns, particularly with
blockwise missing structures that are commonly observed
in mental health databases. This study also systematically
assessed the latest missing data imputation approaches
like MIDAS. The limitation is that the complete data with
missing data simulation primarily comes from adolescents.
Despite the inclusion of various racial groups in the
simulation, most participants are white. Assessment in
other types of large-scale mental and behavioral surveys
with adults and minority groups is warranted for future
studies.
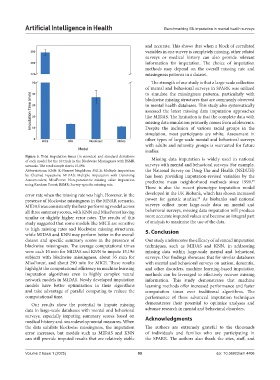
Figure 5. Total imputation times (in minutes) and standard deviations Missing data imputation is widely used in national
of each model for the 10 trials in the Blockwise Missingness with BSMR
scenario. The total sample size is 15,196. surveys with mental and behavioral surveys. For example,
Abbreviations: KNN: K-Nearest Neighbors; MICE: Multiple Imputation the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH)
by Chained Equations; MIDAS: Multiple Imputation with Denoising has been providing imputation-revised variables by the
Autoencoders; MissForest: Non-parametric missing value imputation predictive mean neighborhood methods since 1999.
29
using Random Forest; BSMR: Survey-specific missing rate.
There is also the recent phenotype imputation model
error rate when the missing rate was high. However, in the developed in the UK Biobank, which has shown increased
30
presence of blockwise missingness in the MNAR scenario, power for genetic studies. As biobanks and national
MIDAS was consistently the best-performing model across surveys collect more large-scale data on mental and
all three summary scores, with KNN and MissForest having behavioral surveys, missing data imputation will produce
similar or slightly higher error rates. The results of this more accurate imputed values and become an integral part
study suggested that some models like MICE are sensitive of analysis to maximize the use of the data.
to high missing rates and blockwise missing structures, 5. Conclusion
while MIDAS and KNN may perform better in the overall
dataset and specific summary scores in the presence of Our study underscores the efficacy of advanced imputation
blockwise missingness. The average computational times techniques, such as MIDAS and KNN, in addressing
were each 10 min for MIDAS and KNN to impute 15,196 missing data within large-scale mental and behavioral
subjects with blockwise missingness, about 35 min for surveys. Our findings showcase that for similar databases
MissForest, and about 290 min for MICE. These results with mental and behavioral surveys on autism, dementia,
highlight the computational efficiency in machine learning and other disorders, machine learning-based imputation
imputation algorithms even in highly complex neural methods can be leveraged to effectively recover missing
network models in MIDAS. Newly developed imputation information. This study demonstrates that machine
models have better optimization in their algorithms learning methods offer increased performance and faster
and take advantage of parallel computing to reduce the computation times over traditional algorithms. The
computational time. performance of these advanced imputation techniques
Our results show the potential to impute missing demonstrates their potential to optimize analyses and
data in large-scale databases with mental and behavioral advance research in mental and behavioral disorders.
surveys, especially imputing summary scores based on Acknowledgments
medical history and neurodevelopmental measures. When
the data exhibits blockwise missingness, the imputation The authors are extremely grateful to the thousands
error increases, but models such as MIDAS and KNN of individuals and families who are participating in
can still provide imputed results that are relatively stable the SPARK. The authors also thank the sites, staff, and
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 90 doi: 10.36922/aih.4406