Page 138 - AIH-2-3
P. 138
Artificial Intelligence in Health Early detection of CIN/cervicitis using ML
users sharing their screening data and pathology results
with the ML algorithm, its robustness in providing
feedback on tissue status would increase over time, leading
to a more accurate, objective, and real-time tool for cervical
cancer screening. With the availability of a larger data set,
a supervised ML algorithm with SVM could be configured
to classify different grades of cervical cancer, such as LSIL,
HSIL, and CIN grades 1, 2, and 3, as well as carcinoma
in situ. The SVM classifies the data by identifying the best
line to separate data points, with the support vectors being
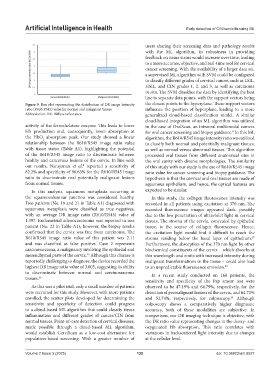
Figure 9. Box plot representing the distribution of DR image intensity the closest points to the hyperplane. These support vectors
ratio (R610/R545) value for normal and malignant tissues influence the position of hyperplane, leading to a more
Abbreviation: DR: Diffuse reflectance. generalized cloud-based classification model. A similar
cloud-based integration of an ML algorithm was utilized
activity of the ferrochelatase enzyme. This leads to lower in the case of OralScan, an intraoral multimodal camera
Hb production and, consequently, lower absorption at for oral cancer screening and biopsy guidance. In this ML
8
the HbO absorption peak. Our study showed a linear algorithm, the R610/R545 image intensity ratio was utilized
2
relationship between the R610/R545 image ratio value to classify both normal and potentially malignant tissues,
with tissue status (Table A1), highlighting the potential as well as normal versus abnormal tissues. This algorithm
of the R610/R545 image ratio to discriminate between processed oral tissues from different anatomical sites in
healthy and cancerous lesions of the cervix. In line with the oral cavity with diverse morphologies. The similarity
our results, Narayanan et al. reported a sensitivity of of this study with our study is the use of R610/R545 image
8
82.2% and specificity of 96.63% for the R610/R545 image ratio value for cancer screening and biopsy guidance. The
ratio to discriminate oral potentially malignant lesions hypothesis is that the cervical and oral tissues are made of
from normal tissues. squamous epithelium, and hence, the optical features are
In this analysis, squamous metaplasia occurring at expected to be similar.
the squamocolumnar junction was considered healthy. In this study, the collagen fluorescence intensity was
Two patients (No. 19 and 21 in Table A1) diagnosed with recorded in all patients using excitation at 370 nm. The
squamous metaplasia were classified as true negatives, recorded fluorescence images appeared dark, possibly
with an average DR image ratio (R610/R545) value of due to the low penetration of ultraviolet light in cervical
1.397. Endometrial adenocarcinoma was reported in one tissues. The stroma of the cervix, concealed by epithelial
patient (No. 22 in Table A1); however, the biopsy results tissue, is the source of collagen fluorescence. Hence,
confirmed that the cervix was free from carcinoma. The the excitation light would find it difficult to reach the
R610/R545 image ratio value of this patient was 2.11 stroma residing below the basal layer of epithelium.
27
and was classified as false positive. Case 2 represents Furthermore, the absorption of the 370 nm light by other
carcinosarcoma, a malignancy involving the epithelial and biochemical constituents of the cervix – which absorbs at
25
mesenchymal parts of the cervix. Although this disease is this wavelength and emits with increased intensity during
reportedly challenging to diagnose, the device recorded the malignant transformations in the tissue – could also lead
highest DR image ratio value of 3.005, suggesting its ability to an unpredictable fluorescence emission. 28
to discriminate between normal and carcinosarcoma In a recent study conducted on 160 patients, the
tissues. 26
sensitivity and specificity of the Pap smear test were
As this was a pilot trial, only a small number of patients observed to be 47.19% and 64.79%, respectively, for the
were recruited for this study. However, with more patients detection of premalignant lesions of the cervix, and 64.72%
enrolled, the scatter plots developed for determining the and 52.74%, respectively, for colposcopy. Although
29
sensitivity and specificity of detection could progress colposcopy shows a comparatively higher diagnostic
to a cloud-based ML algorithm that could classify tissue accuracy, both of these modalities are subjective. In
inflammation and different grades of cancer/CIN from comparison, our DR imaging technique is objective, with
normal tissues. Point-of-care detection of cervical diseases, the DR ratio value representing changes in the deoxy- and
made possible through a cloud-based ML algorithm, oxygenated Hb absorption. This ratio correlates with
would establish CerviScan as a low-cost alternative for variations in backscattered light intensity due to changes
population-based screening. With a greater number of at the cellular level.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 132 doi: 10.36922/aih.8527