Page 11 - AIH-2-4
P. 11
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI in acute stroke imaging
A B
C D
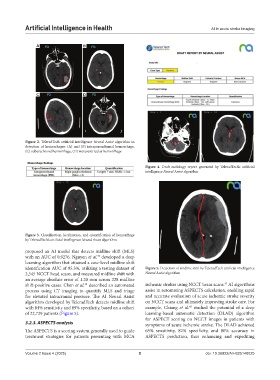
Figure 2. TeleradTech artificial intelligence Neural Assist algorithm in
detection of hemorrhages: (A) and (B) intraparenchymal hemorrhage,
(C) subarachnoid hemorrhage, (D) intraventricular hemorrhage
Figure 4. Draft radiology report generated by TeleradTech’s artificial
intelligence Neural Assist algorithm
Figure 3. Classification, localization, and quantification of hemorrhage
by TeleradTech’s artificial intelligence Neural Assist algorithm
proposed an AI model that detects midline shift (MLS)
with an AUC of 0.9276. Nguyen et al. developed a deep
39
learning algorithm that attained a case-level midline shift
identification AUC of 95.3%, utilizing a testing dataset of Figure 5. Detection of midline shift by TeleradTech artificial intelligence
2,545 NCCT head scans, and measured midline shift with Neural Assist algorithm
an average absolute error of 1.20 mm across 228 midline
shift-positive cases. Chen et al. described an automated ischemic strokes using NCCT brain scans. AI algorithms
42
40
process using CT imaging to quantify MLS and triage assist in automating ASPECTS calculation, enabling rapid
for elevated intracranial pressure. The AI Neural Assist and accurate evaluation of acute ischemic stroke severity
algorithm developed by TeleradTech detects midline shift on NCCT scans and ultimately improving stroke care. For
with 84% sensitivity and 89% specificity, based on a cohort example, Chiang et al. studied the potential of a deep
43
of 22,729 patients (Figure 5). learning-based automatic detection (DLAD) algorithm
for ASPECT scoring on NCCT images in patients with
3.2.3. ASPECTS analysis symptoms of acute ischemic stroke. The DLAD achieved
The ASPECTS is a scoring system generally used to guide 65% sensitivity, 82% specificity, and 80% accuracy in
treatment strategies for patients presenting with MCA ASPECTS prediction, thus enhancing and expediting
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/AIH025140025