Page 12 - AIH-2-4
P. 12
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI in acute stroke imaging
physician decision-making. Upadhyay et al. evaluated demonstrated that AI tools can precisely identify LVO
44
an AI algorithm for automated ASPECT scoring, which on CTA in real time. 49-53 Le et al. demonstrated that a
50
decreased diagnosis time for NCCT scans and demonstrated machine learning algorithm used for automated LVO
a 76.19% agreement with radiologists. AI-assisted ASPECT detection on CTA, coupled with secure communication at
scoring systems have shown outcomes comparable to, non-EVT-performing primary stroke centers, significantly
or in some cases better than, manual assessments by reduced door-in-door-out time by promptly alerting
clinicians. They demonstrate good to excellent reliability, clinicians. This intervention increased the number
with intraclass correlation coefficients indicating strong of patients undergoing EVT after transfer, ultimately
agreement with expert consensus and reference standards. improving patient outcomes. In a retrospective study by
In a study by Maegerlein et al., AI-generated ASPECTS Rodrigues et al. found that the AI Viz-LVO Algorithm ®
45
51
in acute MCA stroke showed better agreement with version 1.4 detected internal carotid artery and MCA-M1
predefined consensus scores than human readers alone. LVOs with a sensitivity of 87.6%, specificity of 88.5%, and
AI tools not only reduce inter-observer variability but also accuracy of 87.9% (AUC 0.88). Similarly, Rava et al., in a
52
enhance clinical decision-making by providing quick and study on acute ischemic stroke patients, reported that the
reliable ASPECT scores, which are critical for assessing AUTO Stroke Solution LVO achieved 73% sensitivity, 98%
the severity of acute ischemic stroke and determining specificity, and 81% accuracy in correctly identifying and
patient eligibility for treatments like thrombectomy and localizing LVOs. The accuracy, sensitivity, and Matthews
thrombolysis. 46,47 Additionally, features such as heat maps correlation coefficients of the algorithm for detecting
indicate the probability of low attenuation and sulcal different occlusion types were as follows: 0.95, 0.90, and
effacement. 0.89, respectively, for the internal carotid artery; 0.89, 0.77,
and 0.78, respectively, for the M1 segment of the MCA; and
3.2.4. MCA
0.80, 0.51, and 0.59, respectively, for the M2 segment of the
In a study conducted by Shinohara et al. on a cohort MCA. Additionally, the RAPID CTA AI solution showed
48
of patients with acute ischemic stroke, the diagnostic strong potential in detecting intracranial LVO, with a
performance of a deep convolutional neural network sensitivity of 94% and specificity of 76%, as revealed in a
model (Xception) was evaluated for the identification and study conducted by Amukotuwa et al. 53
prioritization of the hyperdense MCA sign on NCCT. The
model demonstrated a sensitivity of 82.9%, specificity of 3.3. Perfusion analysis
89.7%, and accuracy of 86.5% using leave-one-case-out CT perfusion (CTP) imaging has emerged as a key
cross-validation. Furthermore, the AI Neural Assist imaging technique for assessing acute ischemic stroke and
algorithm developed by TeleradTech detected dense MCA determining eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval in
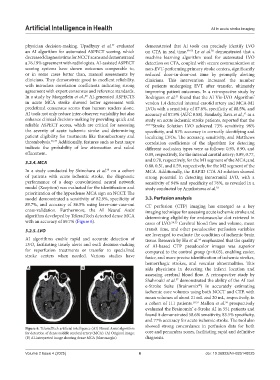
with an accuracy of 89.7% (Figure 6). cases of LVO. 54,55 Cerebral blood flow and volume, mean
3.2.5. LVO transit time, and other pseudocolor perfusion variables
are leveraged to evaluate the condition of ischemic brain
AI algorithms enable rapid and accurate detection of tissue. Research by Hu et al. emphasized that the quality
56
LVO, facilitating timely alerts and swift decision-making of AI-based CTP pseudocolor images was superior
for reperfusion treatments or transfer to specialized compared to the control group (p<0.05), enabling easier,
stroke centers when needed. Various studies have faster, and more precise identification of ischemic strokes,
hemorrhagic strokes, and vascular abnormalities. This
A B aids physicians in detecting the infarct location and
assessing cerebral blood flow. A retrospective study by
Shahrouki et al. demonstrated the ability of the AI tool
57
e-Stroke Suite (Brainomix ) in accurately estimating
®
ischemic core volumes using both NCCT and CTP, with
mean volumes of about 21 mL and 20 mL, respectively, in
a cohort of 111 patients. 19,57 Mallon et al. prospectively
58
evaluated the Brainomix e-Stroke AI in 551 patients and
®
found it demonstrated 58.6% sensitivity, 83.5% specificity,
and 77% accuracy for acute ischemic stroke. The tool also
showed strong concordance in perfusion data for both
Figure 6. TeleradTech artificial intelligence (AI) Neural Assist algorithm
for detection of dense middle cerebral artery (MCA): (A) Original image; core and penumbra zones, facilitating rapid and definitive
(B) AI-interpreted image showing dense MCA (blue margin) diagnosis.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/AIH025140025