Page 136 - AIH-2-4
P. 136
Artificial Intelligence in Health Artificial intelligence app for EVD navigation
1. Introduction divert cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for both therapeutic
and diagnostic purposes. It is most commonly used to
Surgical navigation has become a crucial tool in neurosurgery, manage elevated intracranial pressure in conditions such
enabling accurate localization and targeting of lesions as subarachnoid hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, and
within the brain and spine to improve surgical precision and hydrocephalus. EVDs allow continuous monitoring of
41
1-3
patient outcomes. While traditional navigation methods intracranial pressure and facilitate sampling of CSF to
relied on intraoperative imaging, computer-assisted guide treatment of structural obstructions, hemorrhage-
navigation systems have become increasingly common and related complications, and other conditions. 42
4-7
popular. These systems, however, typically require costly,
proprietary computing to run navigation software and are The placement procedures involve incising the scalp
often bulky and cumbersome. and drilling a small burr hole, typically at Kocher’s point—
approximately 10–11 cm posterior to the nasion and 2–3 cm
Innovations in computation, particularly artificial lateral to the midline—followed by careful advancement of
intelligence (AI), have paved the way for the development a catheter 6–7 cm until CSF return is noted. This location
of higher-accuracy, lower-cost navigation techniques. is presumed to be in the ipsilateral lateral ventricle near the
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), in particular, foramen of Monro, which connects the lateral ventricles to
have revolutionized image recognition across industries, the inferior third ventricle. The catheter is then tunneled
43
including neurosurgery. 8-10 CNNs are neural network-based subcutaneously for at least 6 cm to reduce infection risk,
machine learning, also known as deep learning models, secured with stitches or staples, and connected to an
that are now the standard for computer vision, particularly external drainage and intracranial pressure monitoring
for identifying and recognizing objects or features via system. Most institutions confirm placement with a post-
pixel analysis. 11-13 In neurosurgery, CNN applications operative brain CT scan (Figure 1). Despite its ubiquity
43
include, but are not limited to, automatic segmentation in neurocritical care, EVD placement carries notable
of vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs in magnetic risks, including hemorrhage, infection, and malposition.
resonance imaging (MRI) 14-17 and computed tomography Misplacement of EVDs is associated with higher infection
(CT), measurement of Cobb angles from X-rays, 19,20 and hemorrhage rates, the need for revision procedures,
18
diagnosis of vertebral fractures, enhanced diagnosis increased healthcare costs, and prolonged hospital stay
21
and classification of brain tumors, 22,23 and intraoperative (PMID: 36434852). 41
co-registration of two-dimensional and three-dimensional
24
(3D) imaging. AI-based navigation software powered by EVD placement has the potential to be optimized
U-Net can improve efficiency and performance, potentially by AI-based neuronavigation. AI navigation tools have
eliminating the need for expensive, cumbersome hardware already been integrated into other specialties for bedside
in the operating room or at the bedside. procedures, such as ultrasound-guided vascular access and
More recently, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as
a valuable tool for facilitating surgical care in the operating
room and beyond. AR merges real-world images with virtual
25
objects generated by computer graphics in real time. In the
operating room, AR has found applications in visualizing
tumors and surrounding anatomical structures in a number
of oncological settings to facilitate safe resection. 26-34 In
neurosurgery, AR applications include guiding pedicle screw
placement in spine surgery and visualizing anatomy during
minimally invasive surgery. 35-38 Outside the operating room,
AR has proven effective in surgical and medical education,
including virtual surgical training. 39,40
Bedside neurosurgical procedures represent a setting
where such navigational innovations could be particularly
beneficial, as limited space and urgent or emergent
scenarios often preclude the use of traditional operating
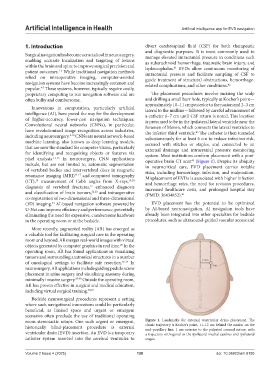
room stereotactic setups. One such urgent or emergent, Figure 1. Landmarks for external ventricular drain placement. The
historically blind-placement procedure is external classic trajectory is Kocher’s point, 11–12 cm behind the nasion on the
mid-pupillary line, 1 cm anterior to the palpated coronal suture, with
ventricular drain (EVD) insertion. An EVD is a temporary a trajectory orthogonal to the ipsilateral medial canthus and ipsilateral
catheter system inserted into the cerebral ventricles to tragus.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 130 doi: 10.36922/aih.8195