Page 16 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 16
Rajak, et al.
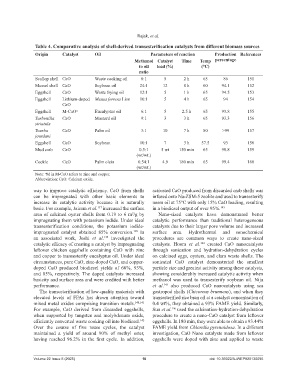
Table 4. Comparative analysis of shell‑derived transesterification catalysts from different biomass sources
Origin Catalyst Oil Parameters of reaction Production References
Methanol Catalyst Time Temp percentage
to oil load (%) (°C)
ratio
Scallop shell CaO Waste cooking oil 6:1 5 2 h 65 86 151
Mussel shell CaO Soybean oil 24:1 12 8 h 60 94.1 152
Eggshell CaO Waste frying oil 12:1 5 1 h 65 94.5 153
Eggshell Lithium-doped Mesua ferrera Linn 10:1 5 4 h 65 94 154
CaO
Eggshell M-CaO a Eucalyptus oil 6:1 5 2.5 h 65 93.8 155
Turbonilla CaO Mustard oil 9:1 3 3 h 65 93.3 156
striatula
Tourbo CaO Palm oil 3:1 10 7 h 80 >99 157
jourdani
Eggshell CaO Soybean 10:1 7 3 h 57.5 93 158
Mud crab CaO 0.5:1 5 wt 150 min 65 98.8 159
(wt/wt.)
Cockle CaO Palm olein 0.54:1 4.9 180 min 65 99.4 160
(wt/wt.)
a
Note: M in M-CaO refers to zinc and copper.
Abbreviation: CaO: Calcium oxide.
way to improve catalytic efficiency. CaO from shells activated CaO produced from discarded crab shells was
can be impregnated with other basic elements to infused onto Na-ZSM-5 zeolite and used to transesterify
increase its catalytic activity because it is naturally neem oil at 75°C with only 15% CaO loading, resulting
basic. For example, Jairam et al. increased the surface in a biodiesel output of over 95%. 143
137
area of calcined oyster shells from 0.19 to 6 m /g by Nano-sized catalysts have demonstrated better
2
impregnating them with potassium iodide. Under ideal catalytic performance than traditional heterogeneous
transesterification conditions, the potassium iodide- catalysts due to their larger pore volume and increased
impregnated catalyst obtained 85% conversion. In surface area. Hydrothermal and sonochemical
138
an associated work, Joshi et al. investigated the procedures are common ways to create nano-sized
139
catalytic efficacy of creating a catalyst by impregnating catalysts. Hoora et al. created CaO nanocatalysts
144
leftover chicken eggshells containing CaO with zinc through sonication and hydration-dehydration cycles
and copper to transesterify eucalyptus oil. Under ideal on calcined eggs, oysters, and clam waste shells. The
circumstances, pure CaO, zinc-doped CaO, and copper- sonicated CaO catalyst demonstrated the smallest
doped CaO produced biodiesel yields of 68%, 93%, particle size and greatest activity among these catalysts,
and 85%, respectively. The doped catalysts increased showing considerably increased catalytic activity when
basicity and surface area and were credited with better methanol was used to transesterify soybean oil. Niju
performance. et al. also produced CaO nanocatalysts using sea
145
The transesterification of low-quality materials with gastropod shells (Chicoreus brunneus), and when they
elevated levels of FFAs has drawn attention toward transesterified rice bran oil at a catalyst concentration of
mixed metal oxides comprising transition metals. 140,141 0.4 wt%, they obtained a 93% FAME yield. Similarly,
For example, CaO derived from discarded eggshells, Sun et al. used the calcination-hydration-dehydration
146
when supported by tungsten and molybdenum oxide, procedure to create a nano-CaO catalyst from leftover
efficiently converted waste cooking oil into biodiesel. eggshells. In 180 min, they were able to obtain a 93.44%
142
Over the course of five reuse cycles, the catalyst FAME yield from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. In a different
maintained a yield of around 90% of methyl ester, investigation, CaO Nano catalysts made from leftover
having reached 96.2% in the first cycle. In addition, eggshells were doped with zinc and applied to waste
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 10 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025130095