Page 216 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 216
Suram, et al.
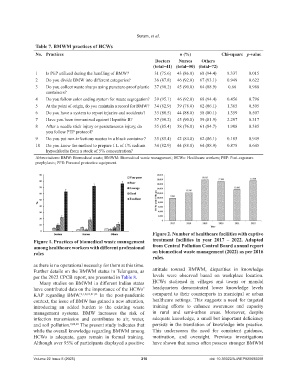
Table 7. BMWM practices of HCWs
No. Practices n (%) Chi‑square p‑value
Doctors Nurses Others
(total=41) (total=50) (total=72)
1 Is PEP utilized during the handling of BMW? 31 (75.6) 43 (86.0) 68 (94.4) 8.337 0.015
2 Do you divide BMW into different categories? 36 (87.8) 46 (92.0) 67 (93.1) 0.949 0.622
3 Do you collect waste sharps using puncture-proof plastic 37 (90.2) 45 (90.0) 64 (88.9) 0.66 0.968
containers?
4 Do you follow color coding system for waste segregation? 39 (95.1) 46 (92.0) 68 (94.4) 0.456 0.796
5 At the point of origin, do you maintain a record for BMW? 34 (82.9) 39 (78.0) 62 (86.1) 1.365 0.505
6 Do you have a system to report injuries and accidents? 33 (80.5) 44 (88.0) 58 (80.1) 1.359 0.507
7 Have you been immunized against Hepatitis B? 37 (90.2) 45 (90.0) 59 (81.9) 2.297 0.317
8 After a needle stick injury or percutaneous injury, do 35 (85.4) 38 (76.0) 61 (84.7) 1.908 0.385
you follow PEP protocol?
9 Do you put non-infectious wastes in a black container? 35 (85.4) 42 (84.0) 62 (86.1) 0.105 0.949
10 Do you know the method to prepare 1 L of 1% sodium 34 (82.9) 44 (88.0) 64 (88.9) 0.878 0.645
hypochlorite from a stock of 5% concentration?
Abbreviations: BMW: Biomedical waste; BMWM: Biomedical waste management; HCWs: Healthcare workers; PEP: Post-exposure
prophylaxis; PPE: Personal protective equipment.
Figure 2. Number of healthcare facilities with captive
Figure 1. Practices of biomedical waste management treatment facilities in year 2017 – 2022. Adapted
among healthcare workers with different professional from Central Pollution Control Board annual report
roles on biomedical waste management (2022) as per 2016
rules.
as there is no operational necessity for them at this time.
Further details on the BMWM status in Telangana, as attitude toward BMWM, disparities in knowledge
per the 2022 CPCB report, are presented in Table 8. levels were observed based on workplace location.
Many studies on BMWM in different Indian states HCWs stationed in villages and towns or mandal
have contributed data on the importance of the HCWs’ headquarters demonstrated lower knowledge levels
KAP regarding BMW. 2,7,8,10,21,23 In the post-pandemic compared to their counterparts in municipal or urban
context, the issue of BMW has gained a new attention, healthcare settings. This suggests a need for targeted
introducing an added burden to the existing waste training efforts to enhance awareness and capacity
management systems. BMW increases the risk of in rural and semi-urban areas. Moreover, despite
infection transmission and contributes to air, water, adequate knowledge, a small but important deficiency
and soil pollution. 9,24,25 The present study indicates that persists in the translation of knowledge into practice.
while the overall knowledge regarding BMWM among This underscores the need for consistent guidance,
HCWs is adequate, gaps remain in formal training. motivation, and oversight. Previous investigations
Although over 95% of participants displayed a positive have shown that nurses often possess stronger BMWM
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 210 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025090058