Page 25 - AN-2-3
P. 25
Advanced Neurology The role of gut in multiple sclerosis
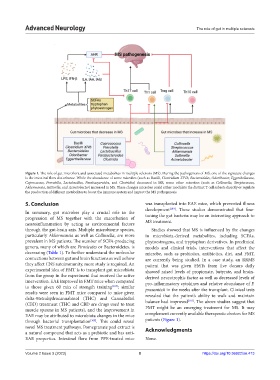
Figure 1. The role of gut microflora and associated metabolites in multiple sclerosis (MS). During the pathogenesis of MS, one of the signature changes
is the intestinal flora disturbance. While the abundance of some microbes (such as Bacilli, Clostridium XIVb, Bacteroidales, Odoribacter, Eggerthellaceae,
Coprococcus, Prevotella, Lactobacillus, Parabacyeroides, and Clostridia) decreased in MS, some other microbes (such as Collinsella, Streptococcus,
Akkermansia, Sutterella, and Acinetobacter) increased in MS. These changes microbes could either modulate the distinct T cell subsets directly or regulate
the production of different metabolites to boost the immune system and impact the MS pathogenesis.
5. Conclusion was transplanted into EAE mice, which prevented illness
development [109] . These studies demonstrated that fine-
In summary, gut microbes play a crucial role in the tuning the gut bacteria may be an interesting approach to
progression of MS together with the exacerbation of
neuroinflammation by acting as environmental factors MS treatment.
through the gut-brain axis. Multiple microbiome species, Studies showed that MS is influenced by the changes
particularly Akkermansia as well as Collinsella, are more in microbiota-derived metabolites, including SCFAs,
prevalent in MS patients. The number of SCFA-producing phytoestrogens, and tryptophan derivatives. In preclinical
genera, many of which are Firmicutes or Bacteroidetes, is models and clinical trials, interventions that affect the
decreasing (Table 1). To further understand the molecular microbe, such as probiotics, antibiotics, diet, and FMT,
connections between gut and brain functions as well as how are currently being studied. In a case study, an RRMS
they affect CNS autoimmunity, more study is required. An patient that was given FMTs from five donors daily
experimental idea of FMT is to transplant gut microbiota showed raised levels of propionate, butyrate, and brain-
from the group in the experiment that received the active derived neurotrophic factor as well as decreased levels of
intervention. EAE improved in FMT mice when compared pro-inflammatory cytokines and relative abundance of F.
to those given 60 min of strength training [107] ; similar prausnitzii in the weeks after the transplant. Clinical tests
results were seen in FMT mice compared to mice given
delta-9tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol revealed that the patient’s ability to walk and maintain
. The above studies suggest that
balance had improved
[110]
(CBD) treatment (THC and CBD are drugs used to treat
muscle spasms in MS patients), and the improvement in FMT might be an emerging treatment for MS. It may
EAE may be attributed to microbiota changes in the mice complement currently available therapeutic choices for MS
through bacterial transplantation [108] . This could reveal patients (Figure 1).
novel MS treatment pathways. Pomegranate peel extract is Acknowledgments
a natural compound that acts as a prebiotic and has anti-
EAE properties. Intestinal flora from PPE-treated mice None.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.413