Page 83 - AN-2-4
P. 83
Advanced Neurology NPRL2 as possible actor in reflex seizures
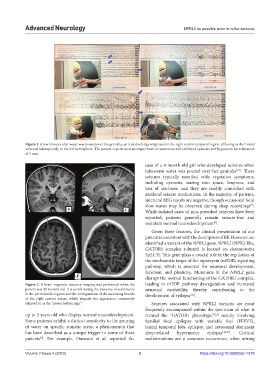
Figure 1. A few minutes after water was poured over the genitalia, an ictal discharge originated in the right central-temporal region, diffusing to the frontal
area and subsequently to the left hemisphere. The patient experienced an impairment of awareness and exhibited cyanosis and hypotonia for a duration
of 1 min.
case of a 4-month-old girl who developed seizures when
lukewarm water was poured over her genitalia . These
[10]
seizures typically manifest with vegetative symptoms,
including cyanosis, staring into space, limpness, and
loss of alertness, and they are readily controlled with
antifocal seizure medications. In the majority of patients,
interictal EEG results are negative, though occasional focal
slow waves may be observed during sleep recordings .
[9]
While isolated cases of non-provoked seizures have been
reported, patients generally remain seizure-free and
maintain normal neurodevelopment .
[9]
Given these features, the clinical presentation of our
patient is consistent with the description of BE. However, we
identified a variant of the NPRL2 gene. NPRL2 (NPR2-like,
GATOR1 complex subunit) is located on chromosome
3p21.31. This gene plays a crucial role in the regulation of
the mechanistic target of the rapamycin (mTOR) signaling
pathway, which is essential for neuronal development,
function, and plasticity. Mutations in the NPRL2 gene
disrupt the normal functioning of the GATOR1 complex,
Figure 2. A brain magnetic resource imaging was performed when the leading to mTOR pathway dysregulation and increased
patient was 20 months old. It is worth noting the presence of asymmetry neuronal excitability, thereby contributing to the
in the perirolandic regions and the configuration of the ascending branch development of epilepsy .
[11]
of the right central sulcus, which imparts the appearance commonly
referred to as the “power button sign.” Seizures associated with NPRL2 variants are most
frequently encompassed within the spectrum of what is
up to 3 years old who display normal neurodevelopment. termed the “GATOR1 phenotype,” mainly involving
[12]
Some patients exhibit a distinct sensitivity to the pouring familial focal epilepsy with variable foci (FFEVF),
of water on specific somatic areas, a phenomenon that lateral temporal lobe epilepsy, and autosomal dominant
has been described as a unique trigger in some of these sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy [12,13] . Cortical
patients . For example, Franzoni et al. reported the malformations are a common occurrence, often arising
[9]
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1379