Page 127 - AN-3-1
P. 127
Advanced Neurology Seizure as the first symptom of CS-DAVF
Figure 3. Abnormal brain wave activity in electroencephalography. The electroencephalogram shows the irregular slow down of background rhythm and
the periodical release of spikes and slow waves in the left hemisphere, which is called the periodic laterialized epileptiform discharges.
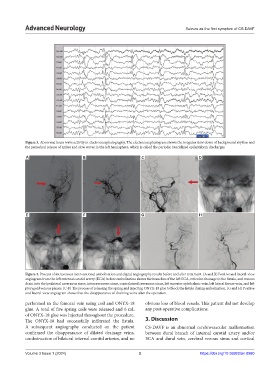
A B C D
E F G H
Figure 4. Process of intravenous interventional embolization and digital angiography results before and after treatment. (A and B) Positive and lateral-view
angiogram from the left external carotid artery (ECA) before embolization shows the branches of the left ECA, reticular drainage to the fistula, and venous
drain into the ipsilateral cavernous sinus, intercavernous sinus, contralateral cavernous sinus, left superior ophthalmic vein, left lateral fissure vein, and left
pterygoid venous plexus. (C-F) The process of releasing the spring and injecting ONYX-18 glue to block the fistula during embolization. (G and H) Positive
and lateral-view angiogram shows that the disappearance of draining veins after the operation.
performed in the femoral vein using coil and ONYX-18 obvious loss of blood vessels. This patient did not develop
glue. A total of five spring coils were released and 6 mL any post-operative complications.
of ONYX-18 glue was injected throughout the procedure.
The ONYX-18 had successfully infiltrated the fistula. 3. Discussion
A subsequent angiography conducted on the patient CS-DAVF is an abnormal cerebrovascular malformation
confirmed the disappearance of dilated drainage veins, between dural branch of internal carotid artery and/or
unobstruction of bilateral internal carotid arteries, and no ECA and dural vein, cerebral venous sinus and cortical
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.0980