Page 102 - AN-3-4
P. 102
Advanced Neurology Shuntogram technique in programmable valves
patency. Ideally, the initial images should display only then every 5 min, as detailed above. The X-ray tube and
this small tracer volume within the reservoir of the shunt, plate can be adjusted caudally as needed to keep the distal
with no proximal or distal flow, although proximal flow injectate within view.
may occur in low-pressure systems. The initial image
review also confirms that the injectate is within the 3. Results and discussion
shunt lumen and not in subcutaneous tissue. If no distal Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the 25 publications
flow is observed within the first 5 – 10 min, the patient discussing shuntogram techniques. These studies exhibit
is then placed upright in a chair or allowed to stand for considerable variability in areas such as patient age,
5 min before re-imaging in the supine position to assess clinical indication, positioning, skin preparation, duration,
for siphoning-related flow. If the flow is still absent and contrast agents, imaging protocols, patency assessment,
a programmable valve is present, the valve should be diagnostic criteria (negative and positive), adjustments
re-read to confirm its setting and reprogrammed to the to shunt flow following positive failure, and measures of
lowest setting if not already set there. Absence of flow after sensitivity and specificity or result/clearance times. Further
these steps indicates an obstruction. As a final adjunctive details are available in Table S1.
step, the shunt reservoir can be manually pumped to In the subsequent discussion, we chronologically
determine whether the obstruction is partial (flow occurs examine the evolution of shuntogram techniques from
under elevated pressure) or complete (no flow despite 1981 to 2024.
pumping). This final step disturbs the steady state of the 9
shunt system and is not used to rule out shunt failure, In 1981, French and Swanson published a study on
but it helps determine if the system remains in continuity radionuclide imaging shuntography to evaluate shunt
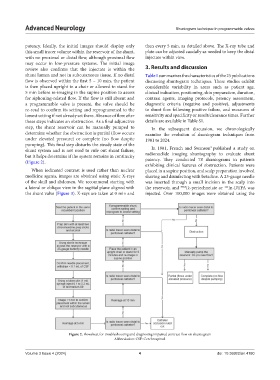
(Figure 2). patency. They conducted 78 shuntograms in patients
exhibiting clinical features of obstruction. Patients were
When iodinated contrast is used rather than nuclear placed in a supine position, and scalp preparation involved
medicine agents, images are obtained using static X-rays shaving and disinfecting with betadine. A 23-gauge needle
of the skull and abdomen. We recommend starting with was inserted through a small incision in the scalp into
a lateral or oblique view in the sagittal plane aligned with the reservoir, and 99m Tc-pertechnetate or In-DTPA was
111
the shunt valve (Figure 3). X-rays are taken at 0 min and injected. Over 100,000 images were obtained using the
Figure 2. Flowsheet for troubleshooting and diagnosing impaired contrast flow on shuntogram
Abbreviation: CSF: Cerebrospinal.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/an.4180