Page 155 - AN-3-4
P. 155
Advanced Neurology Non-invasive electroencephalography in rats
A B
C D E
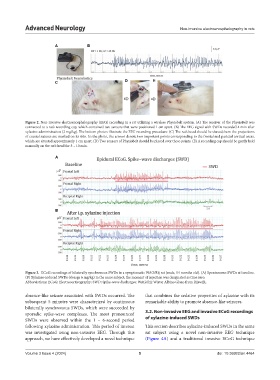
Figure 2. Non-invasive electroencephalography (EEG) recording in a rat utilizing a wireless Physiobelt system. (A) The receiver of the PhysioBelt was
connected to a rat’s recording cap, which contained two sensors that were positioned 1 cm apart. (B) The EEG signal with SWDs recorded 4 min after
xylazine administration (2 mg/kg). The bottom photos illustrate the EEG recording procedure: (C) The rat’s head should be shaved; here the projections
of cranial sutures are marked on its skin. In the photo, the arrows denote two important points corresponding to the frontal and parietal cortical areas,
which are situated approximately 1 cm apart. (D) Two sensors of Physiobelt should be placed over these points. (E) A recording cap should be gently held
manually on the rat’s head for 5 – 10 min.
A
B
Figure 3. ECoG recordings of bilaterally synchronous SWDs in a symptomatic WAG/Rij rat (male, 14 months old). (A) Spontaneous SWDs at baseline.
(B) Xylazine-induced SWDs (dosage 6 mg/kg) in the same subject; the moment of injection was designated as time zero.
Abbreviations: ECoG: Electrocorticography; SWD: Spike-wave discharges; WAG/Rij: Wistar Albino Glaxo from Rijswijk.
absence-like seizure associated with SWDs occurred. The that combines the sedative properties of xylazine with its
subsequent 5 minutes were characterized by continuous remarkable ability to promote absence-like seizures.
bilaterally synchronous SWDs, which were succeeded by
sporadic spike-wave complexes. The most pronounced 3.2. Non-invasive EEG and invasive ECoG recordings
SWDs were observed within the 1 – 6-second period of xylazine-induced SWDs
following xylazine administration. This period of interest This section describes xylazine-induced SWDs in the same
was investigated using non-invasive EEG. Through this rat subject using a novel non-invasive EEG technique
approach, we have effectively developed a novel technique (Figure 4A) and a traditional invasive ECoG technique
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/an.4464