Page 159 - AN-3-4
P. 159
Advanced Neurology Non-invasive electroencephalography in rats
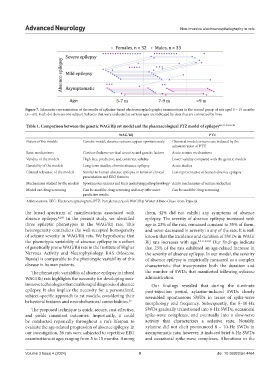
Figure 7. Schematic representation of the results of xylazine-based electroencephalography examinations in the second group of rats aged 5 – 15 months
(n = 65). Each dot denotes one subject. Subjects that were evaluated at various ages are indicated by dots that are connected by lines.
Table 1. Comparison between the genetic WAG/Rij rat model and the pharmacological PTZ model of epilepsy 6,9,11,23,36,38
WAG/Rij PTZ
Nature of the models Genetic model; absence seizures appear spontaneously Chemical model; seizures are induced by the
administration of PTZ
Basic mechanisms Cortico-thalamo-cortical circuitry and genetic factors Acute seizure mechanisms
Validity of the models High face, predictive, and construct validity Lower validity compared with the genetic models
Durability of the models Long-term studies, chronic absence epilepsy Acute studies
Clinical relevance of the models Similar to human absence epilepsy in terms of clinical Less representative of human absence epilepsy
presentation and EEG features
Mechanisms studied by the models Spontaneous seizures and their underlying pathophysiology Acute mechanisms of seizure induction
Model use: drug screening Can be used for drug screening and may offer more Can be used for drug screening
predictive results
Abbreviations: EEG: Electroencephalogram; PTZ: Pentylenetetrazol; WAG/Rij: Wistar Albino Glaxo from Rijswijk.
the broad spectrum of manifestations associated with them, 42% did not exhibit any symptoms of absence
absence epilepsy. 42,43 In the present study, we identified epilepsy. The severity of absence epilepsy increased with
three epileptic phenotypes in the WAG/Rij rats. This age in 23% of the rats, remained constant in 35% of them,
heterogeneity contradicts the well-accepted homogeneity and never decreased in severity in any of the rats. It is well
of seizure severity in WAG/Rij rats. We hypothesize that known that the incidence and duration of SWDs in WAG/
the phenotypic variability of absence epilepsy in a cohort Rij rats increases with age. 8,9,11,32,34 Our findings indicate
of genetically prone WAG/Rij rats in the Institute of Higher that 23% of the rats exhibited an age-related increase in
Nervous Activity and Neurophysiology RAS (Moscow, the severity of absence epilepsy. In our model, the severity
Russia) is comparable to the phenotypic variability of this of absence epilepsy is empirically measured as a complex
disease in human patients. characteristic that incorporates both the duration and
The phenotypic variability of absence epilepsy in inbred the number of SWDs that manifested following xylazine
WAG/Rij rats highlights the necessity for developing non- administration.
invasive technologies that enable rapid diagnosis of absence Our findings revealed that during the 6-minute
epilepsy. It also implies the necessity for a personalized, post-injection period, xylazine-induced SWDs closely
subject-specific approach to rat models, considering their resembled spontaneous SWDs in terms of spike-wave
behavioral features and neurobehavioral comorbidities. 22 morphology and frequency. Subsequently, the 8–10-Hz
The proposed technique is quick, secure, cost-effective, SWDs gradually transitioned into 6-Hz SWDs, occasional
and yields consistent outcomes. Importantly, it could spike-wave complexes, and eventually into a slow-wave
be conducted repeatedly throughout a rat’s lifespan to activity that characterizes a sedative state. Notably,
evaluate the age-related progression of absence epilepsy. In xylazine did not elicit pronounced 8 – 10-Hz SWDs in
our investigation, 26 rats were subjected to repetitive EEG asymptomatic rats; however, it induced brief 6-Hz SWDs
examinations at ages ranging from 5 to 15 months. Among and occasional spike-wave complexes. Alterations in the
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/an.4464