Page 158 - AN-3-4
P. 158
Advanced Neurology Non-invasive electroencephalography in rats
A
B
C
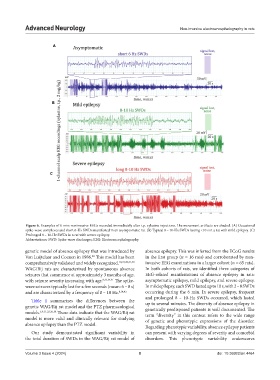
Figure 6. Examples of 6-min noninvasive EEGs recorded immediately after i.p. xylazine injections. The movement artifacts are shaded. (A) Occasional
spike-wave complexes and short 6-Hz SWDs manifested in an asymptomatic rat. (B) Typical 8 – 10-Hz SWDs lasting <10 s in a rat with mild epilepsy. (C)
Prolonged 8 – 10-Hz SWDs in a rat with severe epilepsy.
Abbreviations: SWD: Spike-wave discharges; EEG: Electroencephalography.
genetic model of absence epilepsy that was introduced by absence epilepsy. This was inferred from the ECoG results
29
Van Luijtelaar and Coenen in 1986. This model has been in the first group (n = 16 rats) and corroborated by non-
comprehensively validated and widely recognized. 10,23,30,31,40 invasive EEG examinations in a larger cohort (n = 65 rats).
WAG/Rij rats are characterized by spontaneous absence In both cohorts of rats, we identified three categories of
seizures that commence at approximately 3 months of age, EEG-related manifestations of absence epilepsy in rats:
with seizure severity increasing with age. 8,32,34,41 The spike- asymptomatic epilepsy, mild epilepsy, and severe epilepsy.
wave seizures typically last for a few seconds (mean: 6 – 8 s) In mild epilepsy, each SWD lasted up to 10 s, with 2 – 8 SWDs
and are characterized by a frequency of 8 – 10 Hz. 8,34,41 occurring during the 6 min. In severe epilepsy, frequent
and prolonged 8 – 10-Hz SWDs occurred, which lasted
Table 1 summarizes the differences between the up to several minutes. The diversity of absence epilepsy in
genetic WAG/Rij rat model and the PTZ pharmacological genetically predisposed patients is well documented. The
models. 6,9,11,23,36,38 These data indicate that the WAG/Rij rat term “diversity” in this context refers to the wide range
model is more valid and clinically relevant for studying of genetic and phenotypic expressions of the disorder.
absence epilepsy than the PTZ model. Regarding phenotypic variability, absence epilepsy patients
Our study demonstrated significant variability in can present with varying degrees of severity and comorbid
the total duration of SWDs in the WAG/Rij rat model of disorders. This phenotypic variability underscores
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/an.4464