Page 76 - AN-3-4
P. 76
Advanced Neurology SARS-CoV-2 in age-associated neurodegeneration
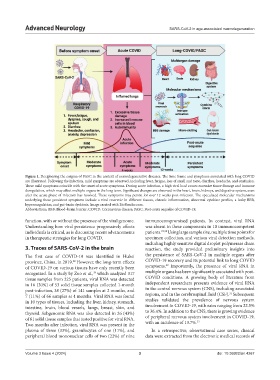
Figure 1. Deciphering the enigma of PASC in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. The time frame and symptoms associated with long COVID
are illustrated. Following the infection, mild symptoms are observed, including fever, fatigue, loss of smell and taste, diarrhea, headache, and confusion.
These mild symptoms coincide with the onset of acute symptoms. During acute infection, a high viral load causes excessive tissue damage and immune
deregulation, which may affect multiple organs in the long term. Significant changes are observed in the heart, brain, kidneys, and digestive system, even
after the acute phase of infection has resolved. These symptoms may persist for over 12 weeks post-infection. The speculated molecular mechanisms
underlying these persistent symptoms include a viral reservoir in different tissues, chronic inflammation, abnormal cytokine profiles, a leaky BBB,
hypercoagulation, and gut-brain dysbiosis. Image created with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: BBB: Blood–brain barrier; COVID: Coronavirus disease; PASC: Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19.
function, with or without the presence of the viral genome. immunocompromised patients. In contrast, viral RNA
Understanding how viral persistence progressively affects was absent in these components in 10 immunocompetent
individuals is critical, as is discussing recent advancements patients. 29,30 Using large sample size, multiple time points for
in therapeutic strategies for long COVID. specimen collection, and various viral detection methods,
including highly sensitive digital droplet polymerase chain
3. Traces of SARS-CoV-2 in the brain reaction, the study provided preliminary insights into
The first case of COVID-19 was identified in Hubei the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in multiple organs after
province, China, in 2019. However, the long-term effects COVID-19 recovery and its potential link to long COVID
28
29
of COVID-19 on various tissues have only recently been symptoms. Importantly, the presence of viral RNA in
29
recognized. In a study by Zuo et al., which analyzed 317 multiple organs has been significantly associated with post-
tissue samples from 225 patients, viral RNA was detected COVID conditions. A growing body of literature from
in 16 (30%) of 53 solid tissue samples collected 1-month independent researchers presents evidence of viral RNA
post-infection, 38 (27%) of 141 samples at 2 months, and in the central nervous system (CNS), including associated
31
7 (11%) of 66 samples at 4 months. Viral RNA was found regions, and in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Subsequent
in 10 types of tissues, including the liver, kidney, stomach, studies validated the prevalence of nervous system
intestine, brain, blood vessels, lungs, breast, skin, and involvement in COVID-19, with rates ranging from 22.5%
thyroid. Subgenomic RNA was also detected in 26 (43%) to 36.4%. In addition to the CNS, there is growing evidence
of 61 solid tissue samples that tested positive for viral RNA. of peripheral nervous system involvement in COVID-19,
32
Two months after infection, viral RNA was present in the with an incidence of 13.7%.
plasma of three (33%), granulocytes of one (11%), and In a retrospective, observational case series, clinical
peripheral blood mononuclear cells of two (22%) of nine data were extracted from the electronic medical records of
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/an.4267