Page 81 - AN-3-4
P. 81
Advanced Neurology SARS-CoV-2 in age-associated neurodegeneration
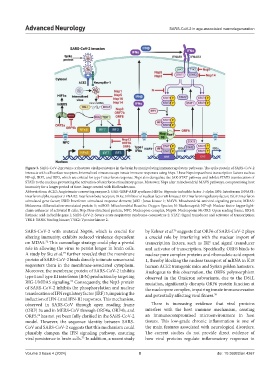
Figure 3. SARS-CoV-2 proteins orchestrate viral persistence in the brain by manipulating immunoregulatory pathways. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2
interacts with cell surface receptors. Internalized viruses escape innate immune responses using Nsps. These Nsps impact host transcription factors such as
NF-κβ, IRF7, and IRF3, which are critical for type I interferon response. Nsps also deregulate the JAK-STAT pathway and inhibit STAT3 translocation of
STATs to the nucleus, preventing the activation of interferon stimulatory genes. Moreover, Nsps alter mitochondrial MAVS pathways, compromising host
immunity for a longer period of time. Image created with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; GAS: GMP-AMP synthase; HIF1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; IFN: Interferons; IFNAR1:
Interferon alpha receptor; IFNAR2: Interferon beta receptor; IKKε: Inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; ISGF: Interferon
stimulated gene factor; ISRE: Interferon stimulated response element; JAK1: Janus kinase 1; MAVS: Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MDA5:
Melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; mtROS: Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species; N: Nucleocapsid; NF-κβ: Nuclear factor kappa-light-
chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Nsp: Non-structural protein; NPC: Nucleopore complex; Nup98: Nucleoporin 98; ORF: Open reading frame; RIG-I:
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription;
TBK1: TANK binding kinase; TYK2: Tyrosine kinase 2.
SARS-CoV-2 with mutated Nsp16, which is crucial for by Kehrer et al. suggests that ORF6 of SARS-CoV-2 plays
76
altering immunity, exhibits reduced virulence dependent a crucial role by interfering with the nuclear import of
on MDA5. This camouflage strategy could play a pivotal transcription factors, such as IRF and signal transducer
72
role in allowing the virus to persist longer in brain cells. and activator of transcription. Specifically, ORF6 binds to
A study by Siu et al. further revealed that the membrane nuclear pore complex proteins and ribonucleic acid export
73
protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds directly to innate sensors and 1, thereby blocking the nuclear transport of mRNA in K18
sequesters them in the membrane-associated cytoplasm. human ACE2 transgenic mice and Syrian golden hamsters.
Moreover, the membrane protein of SARS-CoV-2 inhibits Analogous to this observation, the ORF6 polymorphism
type I and type III interferon (IFN) production by targeting observed in the Omicron subvariants, due to the D61L
RIG-I/MDA5 signaling. Consequently, the Nsp3 protein mutation, significantly disrupts ORF6 protein function at
74
of SARS-CoV-2 inhibits the phosphorylation and nuclear the nucleopore complex, impairing innate immune evasion
translocation of IFN regulatory factor (IRF) 3, impairing the and potentially affecting viral fitness. 76
induction of IFN-I and IFN-III responses. This mechanism,
observed in SARS-CoV through open reading frame There is increasing evidence that viral proteins
(ORF) 3a and in MERS-CoV through ORF4a, ORF4b, and interfere with the host immune mechanism, creating
ORF5, has not yet been fully clarified in the SARS-CoV-2 an immunocompromised microenvironment in host
66
model. However, the sequence identity between SARS- tissues. This low-grade chronic inflammation is one of
CoV and SARS-CoV-2 suggests that this mechanism could the main features associated with neurological disorders.
plausibly dampen the IFN signaling pathway, ensuring The current studies do not provide direct evidence of
viral persistence in brain cells. In addition, a recent study how viral proteins regulate inflammatory responses in
75
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/an.4267