Page 83 - AN-3-4
P. 83
Advanced Neurology SARS-CoV-2 in age-associated neurodegeneration
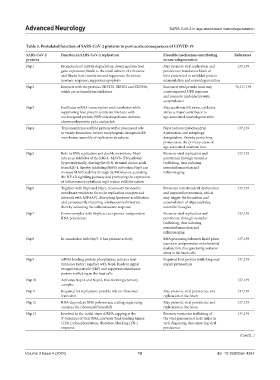
Table 3. Postulated function of SARS‑CoV‑2 proteins in post‑acute consequences of COVID‑19
SARS‑CoV‑2 Function in SARS‑CoV‑2 replication Plausible mechanism contributing References
proteins to neurodegeneration
Nsp1 Promotes host mRNA degradation; downregulates host May promote viral replication and 137,139
gene expression; binds to the small subunit of ribosome persistence; translation block of
and blocks host translation and suppresses the innate host protein led to unfolded protein
immune response; suppresses apoptosis accumulation and neurodegeneration
Nsp2 Interacts with the proteins GIGYF2, EIF4E2 and ZNF598, Increased viral protein load may 70,137,139
which act as translation inhibitors cause impaired UPR response
and promote misfolded protein
accumulation
Nsp3 Facilitates mRNA transcription and translation while May accelerate ER stress, oxidative
suppressing host protein synthesis; interacts with stress, a major contributor to
nucleocapsid protein; PLPro/deubiquitinase domain; age-associated neurodegeneration
cleaves polyprotein pp1a and pp1ab
Nsp4 Transmembrane scaffold protein with a prominent role Nsp4 induces mitochondrial 137,139
in vesicle formation; induce morphogenic changes in ER dysfunction and autophagy
membrane; assembly of replicative structures deregulation, thereby perturbing
proteostasis, the primary cause of
age-associated neuronal loss.
Nsp5 Role in RNA replication and double membrane; Nsp5 Promote viral replication and 137,139
acts as an inhibitor of the RIG-1- MAVS–IFN pathway persistence through vesicular
by proteolytically cleaving the 10 N-terminal amino acids trafficking, thus inducing
from RIG-I, thereby inhibiting MAVS activation; Nsp5 can neuroinflammation and
increase MAVS stability through SUMOylation, activating inflammaging
the NF-κB signaling pathway and promoting the expression
of inflammatory cytokines; nsp5 reduce avSG formation
Nsp6 Together with Nsp3 and Nsp4, it connects the double Promotes mitochondrial dysfunction 137,139
membrane vesicles to form the replication complex and and impaired proteostasis, which
interacts with ATP6AP1, disrupting lysosome acidification may trigger the formation and
and consequently impairing autolysosome formation, accumulation of oligo-peptides,
thereby activating the inflammasome response neurofibril tangles
Nsp7 Forms complex with Nsp8; act as a primer-independent Promote viral replication and 137,139
RNA polymerase persistence through vesicular
trafficking, thus inducing
neuroinflammation and
inflammaging
Nsp8 In association with Nsp7, it has primase activity RNA processing enhances liquid phase 137,139
transition and promotes mitochondrial
dysfunction, thus generating oxidative
stress in the brain cells
Nsp9 ssRNA binding protein phosphatase; acts as a host Impaired host protein trafficking may 137,139
virulence factor; together with Nsp8, binds to signal impair proteostasis
recognition particle (SRP) and suppresses membrane
protein trafficking in the host cells
Nsp10 Activates Nsp14 and Nsp16, thus forming a ternary 137,139
complex
Nsp11 Required for replication; possible role in ribosomal May promote viral persistence and 137,139
frameshift replication in the brain
Nsp12 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; coding sequencing May promote viral persistence and 137,139
contains the ribosomal frameshift replication in the brain
Nsp13 Involved in the initial steps of RNA capping at the Promote versicular trafficking of 137,139
5’-terminus of viral RNA; prevents Tank binding kinase the viral genome in a host; helps in
(TBK1) phosphorylation, therefore, blocking IFN-I viral disguising, thus ensuring viral
response persistence
(Cont’d...)
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 10 doi: 10.36922/an.4267