Page 65 - AN-4-1
P. 65
Advanced Neurology Cognitive assessment using performance-based tests
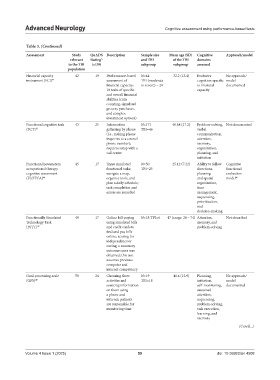
Table 3. (Continued)
Assessment Study QuADS Description Sample size Mean age (SD) Cognitive Approach/model
relevant Rating and TBI of the TBI domains
iv
to the TBI (x/39) subgroup subgroup assessed
population
Financial capacity 42 19 Performance-based N=44 32.2 (13.4) Evaluates No approach/
instrument (FCI) 41 assessment of TBI (moderate cognition specific model
financial capacity; to severe) = 24 to financial documented
18 tasks of specific capacity
and overall financial
abilities (coin
counting, simulated
grocery purchases,
and complex
investment options)
Functional cognitive task 43 25 Information N=171 40.68 (17.2) Problem-solving, Not documented
(FCT) 43 gathering by phone TBI=46 verbal
(i.e., making phone communication,
inquiries to a council attention,
phone number); memory,
requires setup with a organization,
call center planning, and
initiation
Functional Lowenstein 45 17 Three simulated N=50 25.12 (7.22) Ability to follow Cognitive
occupational therapy functional tasks: TBI=25 directions, functional
cognitive assessment navigate a map, planning evaluation
(FLOTCA) 44 organize tools, and and spatial model 46
plan a daily schedule; organization,
task completion and time
errors are recorded management,
sequencing,
prioritization,
and
decision-making
Functionally Simulated 48 17 Online bill-paying N=18 TBI=6 47 (range: 28 – 74) Attention, Not described
Technology Task using simulated bills memory, and
(FSTT) 47 and credit cards to problem-solving
find and pay bills
online; scoring for
independence or
cueing; a summary
outcome score was
obtained; this test
assumes previous
computer and
internet competency
Goal-processing scale 50 24 Choosing three N=19 41.4 (12.9) Planning, No approach/
(GPS) 49 activities and TBI=18 initiation, model
sourcing information self-monitoring, documented
on them using sustained
a phone and attention,
internet; patients sequencing,
are responsible for problem-solving,
monitoring time task execution,
learning, and
memory
(Cont’d...)
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 59 doi: 10.36922/an.4508