Page 70 - AN-4-1
P. 70
Advanced Neurology Cognitive assessment using performance-based tests
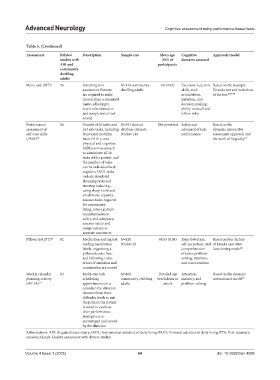
Table 5. (Continued)
Assessment Related Description Sample size Mean age Cognitive Approach/model
studies with (SD) of domains assessed
ABI and participants
community‑
dwelling
adults
Menu task (MT) 5 76 Screening tool N=114 community- 69 (9.85) Executive function Based on the multiple
assessment: Patients dwelling adults skills, such Errands test and variations
are required to make as inhibition, of the test 40,77,78
choices from a simulated initiation, and
menu, adhering to decision-making;
seven rules; initiation ability to recall and
and completion of task follow rules
scored
Performance 80 Consist of 26 tasks and N=941 clinical Not provided Safety and Based on the
assessment of 163 sub-tasks, including database datasets adequacy of task dynamic-interactive
self-care skills functional mobility, Stroke=114 performance assessment approach and
(PASS) 79 basic PADLs, and the work of Vygotsky 81
physical and cognitive
IADLs; not necessary
to administer all 26
tasks with a patient, and
the number of tasks
can be individualized;
cognitive IADL tasks
include simulated
shopping tasks and
stovetop tasks (e.g.,
using sharp knife and
small home repairs);
assesses tasks required
for community
living; rates a patient
on independence,
safety, and adequacy;
assesses safety and
independence as
separate constructs
Pillbox test (PT) 82 82 Medication sorting test: N=120 68.63 (8.08) Error detection, Based on four factors
reading medication Stroke=18 self-correction, and of Lezak’s executive
labels, organizing a comprehension functioning model 62
pillbox/dosette box, of tasks; problem-
and following rules; solving, attention,
errors of omission and and concentration
commission are scored
Weekly calendar 83 Multi-step task N=808 Detailed age Attention, Based on the dynamic
planning activity scheduling community-dwelling breakdown in memory, and interactional model 84
(WCPA) 10 appointments on a adults article problem-solving
calendar; the clinician
chooses from three
difficulty levels to suit
the patient; the patient
is asked to evaluate
their performance;
strategy use is
encouraged and scored
by the clinician
Abbreviations: ABI: Acquired brain injury; IADL: Instrumental activities of daily living; PADL: Personal activities of daily living; PTA: Post-traumatic
amnesia; Quads: Quality assessment with diverse studies.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 64 doi: 10.36922/an.4508