Page 13 - AN-4-2
P. 13
Advanced Neurology Lipid droplets and neurodegenerative disorders
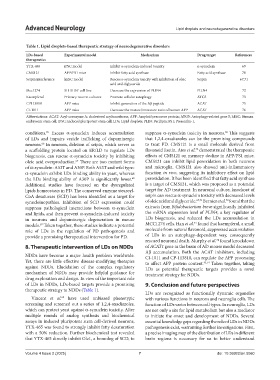
Table 1. Lipid droplets-based therapeutic strategy of neurodegenerative disorders
LDs-based Experimental model Mechanism Drug target References
therapeutics
YTX-465 iPSC model Inhibit α-synuclein-induced toxicity α-synuclein 69
CMS121 APP/PS1 mice Inhibit fatty acid synthase Fatty acid synthase 70
Seipin interference hESC model Rescue a-synuclein toxicity with inhibition of oleic Seipin 67,71
acid and diglyceride
Mcc1274 SH-SH5Y cell line Decrease the expression of PLIN4 PLIN4 72
Kaempferol Primary neuron cultures Promote cellular autophagy ATG5 73
CP113818 APP mice Inhibit generation of the Aβ peptide ACAT 75
CI-1011 APP mice Decrease the mature/immature ratio of human APP ACAT 76
Abbreviations: ACAT: Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase; APP: Amyloid precursor protein; ATG5: Autophagy-related gene 5; hESC: Human
embryonic stem cell; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; LDs: Lipid droplets; PLIN: Perilipin; PS1: Presenilin-1.
conditions. Excess α-synuclein induces accumulation suppress α-synuclein toxicity in neurons. This suggests
65
69
of LDs and impairs vesicle trafficking of dopaminergic that 1,2,4-oxadiazoles can be the promising compounds
neurons. In neurons, deletion of seipin, which serves as to treat PD. CMS121 is a small molecule derived from
66
a scaffolding protein located on ER/LD to regulate LDs flavonoid fisetin. Ates et al. demonstrated the therapeutic
70
biogenesis, can rescue α-synuclein toxicity by inhibiting effects of CMS121 on memory decline in APP/PS1 mice.
oleic acid overproduction. There are two mutant forms CMS121 can inhibit lipid peroxidation in both neurons
67
of α-synuclein: A53T and A30P. Both A53T and wild type- and microglia. CMS121 also showed anti-inflammatory
α-synuclein exhibit LDs binding ability in yeast, whereas function in vivo, suggesting its inhibitory effect on lipid
the LDs binding ability of A30P is significantly lower. peroxidation. It has been identified that fatty acid synthase
68
Additional studies have focused on the dysregulated is a target of CMS121, which was proposed as a potential
lipids homeostasis in PD. The conserved enzyme stearoyl- target for AD treatment. In neuronal culture, knockout of
CoA desaturase (SCD) has been identified as a target for seipin can rescue α-synuclein toxicity with decreased levels
72
synucleinopathies. Inhibition of SCD expression could of oleic acid and diglyceride. 67,71 Bernier et al. found that the
suppress pathological interactions between α-synuclein extracts from Bifidobacterium breve significantly inhibited
and lipids, and then prevent α-synuclein-induced toxicity the mRNA expression level of PLIN4, a key regulator of
in neurons and dopaminergic degeneration in mouse LDs biogenesis, and reduced the LDs accumulation in
73
models. Taken together, these studies indicate a potential MCC1274 cells. Han et al. found that kaempferol, a small
67
role of LDs in the regulation of PD pathogenesis and molecule from natural flavonoid, suppressed accumulation
provide a promising therapeutical intervention for PD. of LDs in an autophagy-dependent way, consequently
rescued neuronal death. Murphy et al. found knockdown
74
8. Therapeutic intervention of LDs on NDDs of ACAT1 gene in the brain of AD mouse model decreased
Aβ accumulation. Both the ACAT inhibitors, including
NDDs have become a major health problem worldwide. CI-1011 and CP-113818, can regulate the APP processing
Yet, there are little effective disease-modifying therapies to affect APP protein content. 43,74 Taken together, taking
against NDDs. Elucidation of the complex regulatory LDs as potential therapeutic targets provides a novel
mechanism of NDDs may provide helpful guidance for treatment strategy for NDDs.
drug exploration and design. In view of the important role
of LDs in NDDs, LDs-based targets provide a promising 9. Conclusion and future perspectives
therapeutic strategy to NDDs (Table 1).
LDs are recognized as functionally dynamic organelles
Vincent et al. have used unbiased phenotypic with various functions in neurons and neuroglia cells. The
69
screening and screened out a series of 1,2,4-oxadiazoles, function of LDs varies between cell types. In neuroglia, LDs
which can protect yeast against α-synuclein toxicity. After are not only a site for lipid metabolism but also a mediator
multiple rounds of analog synthesis and biochemical to initiate the onset and development of NDDs. Several
assays in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons, essential knowledge gaps regarding the role of LDs in NDDs
YTX-465 was found to strongly inhibit fatty desaturation pathogenesis exist, warranting further investigations. First,
with a 50% reduction. Further biochemical test revealed a precise imaging map of the distribution of LDs in different
that YTX-465 directly inhibit Ole1, a homolog of SCD, to brain regions is necessary for us to better understand
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/an.5060