Page 111 - AN-4-3
P. 111
Advanced Neurology ADRD comorbidities and senescence
A B
C D
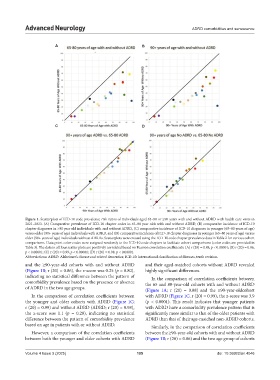
Figure 1. Scatterplots of ICD-10 code prevalence risk ratios of individuals aged 65–80 or ≥90 years with and without ADRD with health care visits in
2021–2023. (A) Comparative prevalence of ICD-10 chapter codes in 65–80 year olds with and without ADRD, (B) comparative incidence of ICD-10
chapter diagnoses in >90 year old individuals with and without ADRD, (C) comparative incidence of ICD-10 diagnoses in younger (65–80 years of age)
versus older (90+ years of age) individuals with ADRD, and (D) comparative incidence of ICD-10 chapter diagnoses in younger (65–80 years of age) versus
older (90+ years of age) individuals without ADRDs. Scatterplots were created using the ICD-10 code chapter prevalence data in Table 2 for various cohort
comparisons. Data point color codes were assigned randomly to the ICD-10 code chapters to facilitate cohort comparisons (color codes are provided in
Table 3). The data in all four scatter plots are positively correlated based on Pearson correlation coefficients: (A) r (20) = 0.88, p < 0.00001; (B) r (20) = 0.86,
p < 0.00001; (C) r (20) = 0.99, p < 0.00001; (D) r (20) = 0.98, p < 0.00001.
Abbreviations: ADRD: Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias; ICD-10: International classification of diseases, tenth revision.
and the ≥90-year-old cohorts with and without ADRD and their aged-matched cohorts without ADRD revealed
(Figure 1B; r (20) = 0.86), the z-score was 0.25 (p = 0.80), highly significant differences.
indicating no statistical difference between the pattern of In the comparison of correlation coefficients between
comorbidity prevalence based on the presence or absence the 65 and 80-year-old cohorts with and without ADRD
of ADRD in the two age groups. (Figure 1A; r (20) = 0.88) and the ≥90-year-oldcohort
In the comparison of correlation coefficients between with ADRD (Figure 1C, r (20) = 0.99), the z-score was 3.9
the younger and older cohorts with ADRD (Figure 1C; (p < 0.0001). This result indicates that younger patients
r (20) = 0.99) and without ADRD (ADRD; r (20) = 0.98), with ADRD have a comorbidity prevalence pattern that is
the z-score was 1.1 (p = 0.28), indicating no statistical significantly more similar to that of the older patients with
difference between the pattern of comorbidity prevalence ADRD than that of their age-matched non-ADRD cohorts.
based on age in patients with or without ADRD. Similarly, in the comparison of correlation coefficients
However, a comparison of the correlation coefficients between the ≥90-year-old cohorts with and without ADRD
between both the younger and older cohorts with ADRD (Figure 1B; r (20) = 0.86) and the two age group of cohorts
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 105 doi: 10.36922/an.4046