Page 40 - AN-4-3
P. 40
Advanced Neurology Depression and its risk factors in India
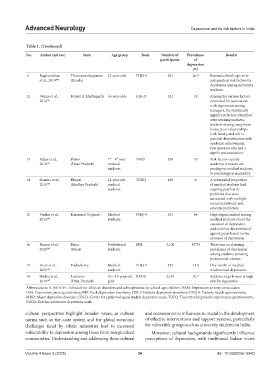
Table 1. (Continued)
No. Author and year State Age group Tools Number of Prevalence Results
participants of
depression
(%)
11 Raghunathan Thiruvananthapuram 22-year-olds PHQ-9 364 26.9 Romantic break-ups were
et al., 2019 160 (Kerala) independent risk factors for
depression among university
students.
12 Verma et al., Raipur (Chhattisgarh) 16-year-olds CES-D 321 19 Among the various factors
2014 161 examined for association
with depression among
teenagers, the statistically
significant factors identified
were working mothers,
students staying away from
home, poor relationships
with family, and self or
parental dissatisfaction with
academic achievement.
Peer pressure also had a
significant association.
13 Yadav et al., Jhansi 1 – 4 year DASS 330 57 Risk factors outside
st
th
2016 162 (Uttar Pradesh) medical academic stressors can
students predispose medical students
to psychological morbidity.
14 Sharma et al., Bhopal 21-year-old TDEQ 440 31 A substantial proportion
2015 163 (Madhya Pradesh) medical of medical students had
students ongoing psychiatric
problems that were
associated with multiple
social, behavioral, and
educational factors.
15 Vankar et al., Karamsad (Gujarat) Medical PHQ-9 331 64 High stigma existed among
2014 164 students medical students about the
causation of depression,
and students discriminated
against peers based on the
presence of depression.
16 Nezam et al., Patna Professional BDI 3,100 47.78 There was an alarming
2020 165 (Bihar) students prevalence of depression
among students pursuing
professional courses.
17 Arun et al., Puducherry Medical PHQ-9 425 13.9 One-fourth of medical
2022 166 students students had depression.
18 Shukla et al., Lucknow 10 – 19-year-old KADS 2,187 39.7 Adolescent girls were at high
2019 167 (Uttar Pradesh) girls risk for depression.
Abbreviations: K-SADS-PL: Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children; DASS: Depression anxiety stress scales;
DAS: Depression, anxiety, and stress; BDI: Beck depression inventory; CDI: Children’s depression inventory; PHQ-9: Patients health questionnaire;
MDD: Major depressive disorder; CES-D: Center for epidemiological studies depression scale; TDEQ: Theoretical depressive experiences questionnaire;
KADS: Kutcher adolescent depression scale.
cultural perspectives highlight broader issues, as cultural and socioeconomic influences is crucial in the development
norms such as the caste system and the global economic of effective interventions and support systems, particularly
challenges faced by ethnic minorities lead to increased for vulnerable groups such as university students in India.
vulnerability to depression among those from marginalized Moreover, cultural backgrounds significantly influence
communities. Understanding and addressing these cultural perceptions of depression, with traditional Indian views
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 34 doi: 10.36922/an.5940