Page 47 - ARNM-1-2
P. 47
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine SUVmax relating to patient and tumor factors
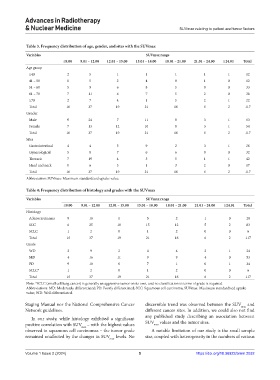
Table 3. Frequency distribution of age, gender, and sites with the SUVmax
Variables SUVmax range
≤9.00 9.01 – 12.00 12.01 – 15.00 15.01 – 18.00 18.01 – 21.00 21.01 – 24.00 ≥24.01 Total
Age group
≤40 2 5 1 1 1 1 1 12
41 – 50 0 5 2 4 0 1 0 12
51 – 60 5 9 6 8 5 0 0 33
61 – 70 7 11 6 7 5 2 0 38
≥70 2 7 4 1 5 2 1 22
Total 16 37 19 21 16 6 2 117
Gender
Male 9 24 7 11 8 3 1 63
Female 7 13 12 10 8 3 1 54
Total 16 37 19 21 16 6 2 117
Sites
Gastrointestinal 4 4 3 9 2 3 1 26
Gynecological 5 8 7 6 6 0 0 32
Thoracic 7 19 4 5 5 1 1 42
Head and neck 0 6 5 1 3 2 0 17
Total 16 37 19 21 16 6 2 117
Abbreviation: SUVmax: Maximum standardized uptake value.
Table 4: Frequency distribution of histology and grades with the SUVmax
Variables SUVmax range
≤9.00 9.01 – 12.00 12.01 – 15.00 15.01 – 18.00 18.01 – 21.00 21.01 – 24.00 ≥24.01 Total
Histology
Adenocarcinoma 9 10 1 5 2 1 0 28
SCC 6 25 18 15 12 5 2 83
SCLC 1 2 0 1 2 0 0 6
Total 16 37 19 21 16 6 2 117
Grade
WD 2 9 2 4 4 2 1 24
MD 4 16 11 9 9 4 0 53
PD 9 10 6 7 1 0 1 34
SCLC* 1 2 0 1 2 0 0 6
Total 16 37 19 21 16 6 2 117
Note: *SCLC (small cell lung cancer) is generally an aggressive tumor on its own, and no classification in terms of grade is required.
Abbreviations: MD: Moderately differentiated; PD: Poorly differentiated; SCC: Squamous cell carcinoma; SUVmax: Maximum standardized uptake
value; WD: Well differentiated.
Staging Manual nor the National Comprehensive Cancer discernible trend was observed between the SUV and
max
Network guidelines. different cancer sites. In addition, we could also not find
any published study describing an association between
In our study, while histology exhibited a significant
positive correlation with SUV max – with the highest values SUV values and the tumor sites.
max
observed in squamous cell carcinomas – the tumor grade A notable limitation of our study is the small sample
remained unaffected by the changes in SUV levels. No size, coupled with heterogeneity in the numbers of various
max
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2032