Page 48 - ARNM-1-2
P. 48
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine SUVmax relating to patient and tumor factors
Table 5. The relationship between various factors with the SUVmax as indicated by Spearman’s correlation and Chi‑square test
Factors SUVmax
Correlation value Pc Linear association by Chi‑square Pc Comment
Age group 0.051 0.583 0.258 0.611 Non-significant
Gender 0.094 0.314 0.802 0.370 Non-significant
System −0.086 0.356 0.871 0.351 Non-significant
Histology 0.237 0.01 5.107 0.024 Significant
Grade −0.064 0.494 0.028 0.867 Non-significant
Stage 0.048 0.608 0.297 0.586 Non-significant
Note: c is based on normal approximation. P<0.05 is statistically significant. Abbreviation: SUVmax: Maximum standardized uptake value.
Table 6. Variables selection and regression analysis factors
Role/function in generalized regression model
Variables selection for regression equation
System Predictor
Age Predictor
Grade Predictor
System Merge categories to maximize association with target
Age Trim outliers
Grade Merge categories to maximize association with target
Results of regression analysis
Variables B (coefficient) Standard error T P
(Constant) 12.728 2.342 5.435 0.000
Age (years) 0.033 0.033 1.017 0.311
Grade 0.158 0.474 0.333 0.739
System -0.515 0.441 -1.167 0.246
Note: P<0.05 is statistically significant.
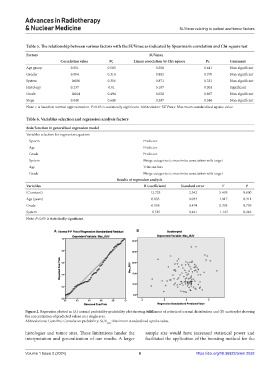
A B
Figure 2. Regression plotted as (A) normal probability-probability plot showing fulfillment of criteria of normal distribution and (B) scatterplot showing
the concentration of predicted values on a single area.
Abbreviations: Cum Pro: Cumulative probability; SUV : Maximum standardized uptake value.
max
histologies and tumor sites. These limitations hinder the sample size would have increased statistical power and
interpretation and generalization of our results. A larger facilitated the application of the boosting method for the
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2032