Page 16 - ARNM-2-1
P. 16
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Blood glucose and I-123 MIBG lung uptake
Diabetes has been linked to the increased uptake and with low-energy, high-resolution collimator, with an
retention of MIBG in the lung due to the dysfunction of energy window of 159 keV ± 7.5, was used in this study.
sympathetic nerve. 7-10 It is also believed that the enhanced I-123 MIBG with a dosage of 110 – 370 MBq was
permeability of the pulmonary endothelial cells could injected slowly through intravenous mode. Whole-body
also increase the uptake of MIBG in the lung. A study planar image, from head to thigh, was acquired at 24-h
11
conducted by Hempel et al. found that high glucose post-injection with bed speed of 6 cm/min.
concentration could increase the permeability of the
endothelial cell. To the best of our knowledge, lung 2.2.2. Image analysis
12
uptake of MIBG in non-diabetic patients has never been
reported in the literature. Image analysis was performed semi-quantitatively
(Figure 2). A region of interest (ROI), measuring 2 × 3 cm ,
2
The aim of this study was to evaluate the correlation was drawn manually and placed on the right-middle
between blood glucose and lung uptake of MIBG and to lung and on the mediastinum to calculate the lung-to-
compare the difference in lung uptake of MIBG between mediastinum ratio (LMR).
diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
2.2.3. Statistical analysis
2. Materials and methods
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
2.1. Materials Pearson’s correlation test was used to evaluate the statistical
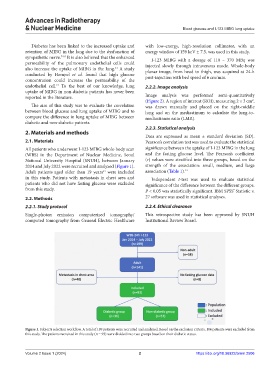
All patients who underwent I-123 MIBG whole-body scan significance between the uptake of I-123 MIBG in the lung
(WBS) in the Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul and the fasting glucose level. The Pearson’s coefficient
National University Hospital (SNUH), between January (r) values were stratified into three groups, based on the
2014 and July 2022 were recruited and analyzed (Figure 1). strength of the association: small, medium, and large
Adult patients aged older than 19 years were included association (Table 1). 14
13
in this study. Patients with metastasis in chest area and Independent t-test was used to evaluate statistical
patients who did not have fasting glucose were excluded significance of the difference between the different groups.
from this study. P < 0.05 was statistically significant. IBM SPSS Statistic v.
®
2.2. Methods 27 software was used in statistical analyses.
2.2.1. Study protocol 2.2.4. Ethical clearance
Single-photon emission computerized tomography/ This retrospective study has been approved by SNUH
computed tomography from General Electric Healthcare Institutional Review Board.
Figure 1. Subjects selection workflow. A total of 199 patients were recruited and analyzed. Based on the exclusion criteria, 106 patients were excluded from
this study. The patients recruited in this study (n = 93) were divided into two groups based on their diabetic status.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2506