Page 19 - ARNM-2-1
P. 19
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Blood glucose and I-123 MIBG lung uptake
prediabetic status and having suffered early CAN would
contribute to the increased lung uptake of MIBG observed
in non-diabetic patients.
This study failed to analyze the correlation of the
increased MIBG uptake in the lung with the effect of
pulmonary cells irradiation. However, this study unveiled
a significant positive correlation with large association
strength between glucose level and lung uptake of MIBG,
regardless of the diabetic status (r = 0.596; P < 0.001). Thus,
a prospective study is warranted to further investigate this
correlation.
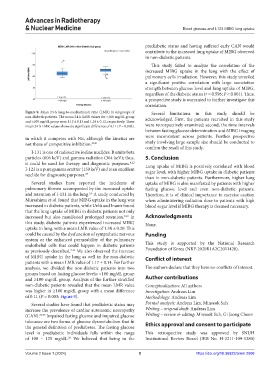
Figure 9. Mean 24-h lung-to-mediastinum ratio (LMR) in subgroups of Several limitations in this study should be
non-diabetic patients. The mean 24-h LMR values for <100 mg/dL group acknowledged. First, the patients recruited in this study
and ≥100 mg/dL group were 1.13 ± 0.13 and 1.24 ± 0.12, respectively. These
mean 24-h LMR values showed a significant difference of 0.11 (P = 0.003). were retrospectively examined; second, the time intervals
between fasting glucose determination and MIBG imaging
in which it competes with NE, although the kinetics are were inconsistent across patients. Further prospective
not those of competitive inhibition. 20,21 study involving large sample size should be conducted to
confirm the result of this study.
I-131 is one of radioactive iodine nuclides. It emits beta
particles (606 keV) and gamma radiation (364 keV); thus, 5. Conclusion
it could be used for therapy and diagnostic purposes. Lung uptake of MIBG is positively correlated with blood
4,22
I-123 is a pure gamma emitter (159 keV) and is an excellent sugar level, with higher MIBG uptake in diabetic patients
nuclide for diagnostic purposes. 23
than in non-diabetic patients. Furthermore, higher lung
Several studies have reported the incidents of uptake of MIBG is also manifested by patients with higher
pulmonary fibrosis accompanied by the increased uptake fasting glucose level and even non-diabetic patients.
and retention of I-131 in the lung. A study conducted by Therefore, it is of clinical importance to exercise caution
5,6
Murashima et al. found that MIBG uptake in the lung was when administering radiation dose to patients with high
increased in diabetic patients, while Unlü and Inanir found blood sugar level if MIBG therapy is deemed necessary.
that the lung uptake of MIBG in diabetic patients not only
increased but also manifested prolonged retention. In Acknowledgments
9,10
this study, diabetic patients experienced increased MIBG None.
uptake in lung, with a mean LMR value of 1.38 ± 0.20. This
could be caused by the dysfunction of sympathetic nervous Funding
system or the enhanced permeability of the pulmonary
endothelial cells that could happen in diabetic patients This study is supported by the National Research
as previously described. 7-11 We also observed the increase Foundation of Korea (NRF-2020R1A2C2011428).
of MIBG uptake in the lung as well in the non-diabetic Conflict of interest
patients with a mean LMR value of 1.17 ± 0.14. For further
analysis, we divided the non-diabetic patients into two The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
groups based on fasting glucose levels: <100 mg/dL group
and ≥100 mg/dL group. Analysis of the further stratified Author contributions
non-diabetic patients revealed that the mean LMR value Conceptualization: All authors
was higher in ≥100 mg/dL group with a mean difference Investigation: Andreas Lim
of 0.11 (P = 0.003; Figure 9). Methodology: Andreas Lim
Several studies have found that prediabetic status may Formal analysis: Andreas Lim, Minseok Suh
increase the prevalence of cardiac autonomic neuropathy Writing – original draft: Andreas Lim
(CAN). 24,25 Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose Writing – review & editing: Minseok Suh, Gi Jeong Cheon
tolerance are two forms of glucose dysmetabolism that fit Ethics approval and consent to participate
the general definition of prediabetes. The fasting glucose
level in prediabetic individuals falls within the range This retrospective study was approved by SNUH
of 100 – 125 mg/dL. We believed that being in the Institutional Review Board (IRB No. H-2211-109-1380)
26
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2506