Page 49 - ARNM-2-1
P. 49
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine SRS after WBRT
significant predictors of survival (P < 0.0007 and P < 0.011, developed distant brain failure, while the rest (six patients)
respectively). Patients with breast cancer had increased with 3 months of follow-up and no distant brain relapse
median survival time of 289 days (9.6 months) compared developed brain metastases (9 metastases in one patient,
to patients with SCLC with a median survival of 127 days 5 in one, 2 in one, and 1 in three).
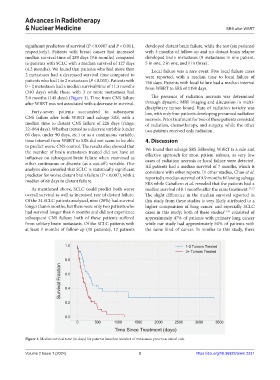
(4.2 months). We found that patients who had more than Local failure was a rare event. Five local failure cases
2 metastases had a decreased survival time compared to were reported, with a median time to local failure of
patients who had 1 to 2 metastases (P < 0.001). Patients with 766 days. Patients with local failure had a median interval
0 – 2 metastases had a median survival time of 11.3 months from WBRT to SRS of 1198 days.
(340 days) while those with 3 or more metastases had
5.0 months (149 days) (Figure 1). Time from CNS failure The presence of radiation necrosis was determined
after WBRT was not associated with a decrease in survival. through dynamic MRI imaging and discussion in multi-
disciplinary tumor board. Rate of radiation toxicity was
Forty-seven patients succumbed to subsequent low, with only four patients developing presumed radiation
CNS failure after both WBRT and salvage SRS, with a necrosis. Prior treatment for two of these patients consisted
median time to distant CNS failure of 226 days (range: of radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery, while the other
22–864 days). Whether treated as a discrete variable (under two patients received only radiation.
60 days, under 90 days, etc.) or as a continuous variable,
time interval from WBRT to SRS did not seem to be able 4. Discussion
to predict worse CNS control. The results also showed that We found that salvage SRS following WBRT is a safe and
the number of brain metastases treated did not have an
influence on subsequent brain failure when examined as effective approach for most patient subsets, as very few
cases of radiation necrosis or local failure were detected.
either continuous or discrete (as a cut-off) variable. Our All patients had a median survival of 7 months, which is
analysis also unveiled that SCLC is statistically significant consistent with other reports. In other studies, Chao et al.
predictor for worse distant brain failure (P < 0.007), with a reported a median survival of 9.9 months following salvage
median of 88 days to distant failure. SRS while Caballero et al. revealed that the patients had a
As mentioned above, SCLC could predict both worse median survival of 8.1 months after the same treatment. 11,13
overall survival as well as increased rate of distant failure. The slight difference in the median survival reported in
Of the 34 SCLC patients analyzed, nine (26%) had survival this study from these studies is very likely attributed to a
longer than 6 months, but there were only two patients who higher composition of lung cancer and especially SCLC
had survival longer than 6 months and did not experience cases in this study; both of these studies 11,13 consisted of
subsequent CNS failure; both of these patients suffered approximately 47% of patients with primary lung cancer
from solitary brain metastasis. Of the SCLC patients with while our study had approximately 60% of patients with
at least 3 months of follow-up (18 patients), 12 patients the same kind of cancer. In similar to this study, there
Figure 1. Median survival time (in days) for patients based on number of metastases present at initial visit.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2231