Page 39 - ARNM-3-1
P. 39
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine EZH2 inhibition in ARID1A-deficient TNBC
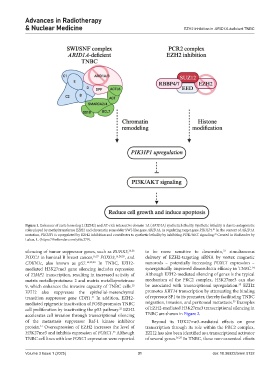
Figure 1. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and AT-rich interactive domain 1A (ARID1A) synthetic lethality. Synthetic lethality is due to antagonistic
21
roles played by methyltransferase EZH2 and chromatin remodeler SWI-like gene ARID1A, in regulating target gene PIK3IP1. In the context of ARID1A
21
mutation, PIK3IP1 is upregulated by EZH2 inhibition and contributes to synthetic lethality by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling. Created in BioRender by
Lukas, L. (https://BioRender.com/y06c279).
silencing of tumor suppressor genes, such as RUNX3, 16,26 to be more sensitive to doxorubin, simultaneous
33
FOXC1 in luminal B breast cancer, 16,27 FOXO3, 16,28,29 , and delivery of EZH2-targeting siRNA by vortex magnetic
CDKN1c, also known as p57. 16,28,30 In TNBC, EZH2- nanorods – potentially increasing FOXC1 expression –
34
mediated H3K27me3 gene silencing includes repression synergistically improved doxorubicin efficacy in TNBC.
of TIMP2 transcription, resulting in increased activity of Although EZH2-mediated silencing of genes is the typical
matrix metalloproteinase 2 and matrix metalloproteinase mechanism of the PRC2 complex, H3K27me3 can also
35
9, which enhances the invasive capacity of TNBC cells. be associated with transcriptional upregulation. EZH2
22
EZH2 also suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal promotes KRT14 transcription by attenuating the binding
31
transition suppressor gene CDH1. In addition, EZH2- of repressor SP1 to its promoter, thereby facilitating TNBC
35
mediated epigenetic inactivation of FOSB promotes TNBC migration, invasion, and peritoneal metastasis. Examples
cell proliferation by inactivating the p53 pathway. EZH2 of EZH2-mediated H3K27me3 transcriptional silencing in
32
accelerates cell invasion through transcriptional silencing TNBC are shown in Figure 2.
of the metastasis suppressor Raf-1 kinase inhibitor Beyond its H3K27me3-mediated effects on gene
protein. Overexpression of EZH2 increases the level of transcription through its role within the PRC2 complex,
31
33
H3K27me3 and inhibits expression of FOXC1. Although EZH2 has also been identified as a transcriptional activator
TNBC cell lines with low FOXC1 expression were reported of several genes. 36,37 In TNBC, these non-canonical effects
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 31 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5132