Page 75 - ARNM-3-2
P. 75
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Modeling renal TAC in dynamic scintigraphy
A The statistical analysis of the results in Table 2 is
summarized in Table 3.
The results and statistical analyses demonstrate that the
free-hand ROI selection method yields significantly lower
T values, indicating a more precise capture of peak tracer
max
B uptake. This method also exhibits a significantly shorter
tracer elimination time, likely due to better exclusion of
background noise. Regarding the 30-min min/max ratio,
the free-hand ROI selection method shows a significantly
lower residual activity, allowing for more accurate isolation
of renal function. Overall, the free-hand ROI selection
method provides physiologically more accurate TACs
by closely contouring kidney anatomy and minimizing
background activity. In contrast, the rectangular ROI
selection method provides consistency across cases but
may include non-kidney regions, which can lead to slightly
overestimated retention values.
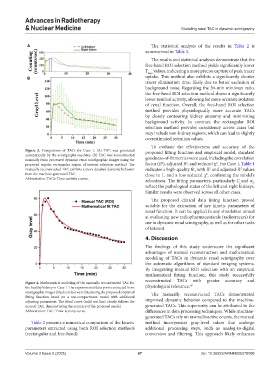
To evaluate the effectiveness and accuracy of the
Figure 3. Comparison of TACs for Case 1. (A) TAC was generated proposed fitting function and empirical model, standard
automatically by the scintigraphy machine. (B) TAC was reconstructed
manually from processed dynamic renal scintigraphic images using the goodness-of-fit metrics were used, including the correlation
2
2
2
proposed regular rectangular region of interest selection method. The factor (R ), adjusted R , and reduced χ . For Case 1, Table 4
manually reconstructed TAC exhibits a more detailed dynamic behavior indicates a high-quality fit, with R and adjusted-R values
2
2
than the machine-generated TAC. close to 1, and a low reduced χ , confirming the model’s
2
Abbreviation: TACs: Time-activity curves. robustness. The fitting parameters, particularly C and α ,
s
s
reflect the pathological status of the left and right kidneys.
Similar results were observed across all other cases.
The proposed clinical data fitting function proved
suitable for the extraction of key kinetic parameters of
renal function. It can be applied in any simulation aimed
at evaluating new radiopharmaceuticals (radiotracers) for
use in dynamic renal scintigraphy, as well as for other tasks
of interest.
4. Discussion
The findings of this study underscore the significant
advantages of manual reconstruction and mathematical
modeling of TACs in dynamic renal scintigraphy over
the automatic algorithms of standard imaging systems.
By integrating manual ROI selection with an empirical
mathematical fitting function, this study successfully
reconstructed TACs with greater accuracy and
Figure 4. Mathematical modeling of the manually reconstructed TAC for 18
the healthy kidney in Case 1. The experimental data points extracted from physiological relevance.
scintigraphic images (black circles) were fitted using the proposed empirical The manually reconstructed TACs demonstrated
fitting function based on a one-compartment model with additional
adjusting parameters. The fitted curve (solid red line) closely follows the improved dynamic behavior compared to the machine-
manual TAC, demonstrating the accuracy of the proposed model. generated TACs. This superiority can be attributed to the
Abbreviation: TAC: Time-activity curve. differences in data processing techniques. While machine-
generated TACs rely on raw radioactive counts, the manual
Table 2 presents a numerical comparison of the kinetic method incorporates gray-level values that undergo
parameters extracted using both ROI selection methods additional processing steps, such as analog-to-digital
(rectangular and free-hand). conversion and filtering. This approach likely enhances
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 67 doi: 10.36922/ARNM025070008