Page 31 - BH-1-2
P. 31
Brain & Heart Autonomic nerve and heart failure
2. Autonomic innervation of the heart rate . Activation of the sympathetic nervous system leads
[20]
to positive chronotropic (heart rate), tropic (conduction
The cardiac autonomic nervous system (CANS) regulates velocity), and inotropic (contractile force) responses. On
the heart in a hierarchical manner that can be divided into the other hand, the activation of the parasympathetic
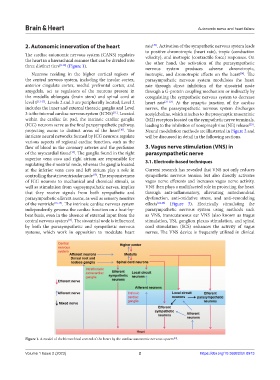
three distinct tiers [8-10] (Figure 1). nervous system produces adverse chronotropic,
Neurons residing in the higher cortical regions of inotropic, and dromotropic effects on the heart . The
[14]
the central nervous system, including the insular cortex, parasympathetic nervous system modulates the heart
anterior cingulate cortex, medial prefrontal cortex, and rate through direct inhibition of the sinoatrial node
amygdala, act as regulators of the neurons present in through a G-protein coupling mechanism or indirectly by
the medulla oblongata (brain stem) and spinal cord at coregulating the sympathetic nervous system to decrease
level 1 [11-13] . Levels 2 and 3 are peripherally located; Level 2 heart rate [21-22] . At the synaptic junction of the cardiac
includes the inner and external thoracic ganglia and Level nerves, the parasympathetic nervous system discharges
3 is the internal cardiac nervous system (ICNS) . Located acetylcholine, which attaches to the presynaptic muscarinic
[11]
within the cardiac fat pad, the intrinsic cardiac ganglia (M2) receptors located on the sympathetic nerve terminals,
(ICG) neurons serve as the final parasympathetic pathway, leading to the inhibition of norepinephrine (NE) release .
[23]
projecting axons to distinct areas of the heart . The Neural modulation methods are illustrated in Figure 2 and
[10]
intricate neural networks formed by ICG neurons regulate will be discussed in detail in the following sections.
various aspects of regional cardiac function, such as the
flow of blood in the coronary arteries and the perfusion 3. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) in
[14]
of the myocardial tissue . The ganglia found in the right parasympathetic nerve
superior vena cava and right atrium are responsible for 3.1. Electrode-based techniques
regulating the sinoatrial node, whereas the ganglia located
at the inferior vena cava and left atrium play a role in Current research has revealed that VNS not only reduces
[15]
controlling the atrioventricular node . The responsiveness sympathetic nervous tension but also directly activates
of ICG neurons to mechanical and chemical stimuli, as vagus nerve efferents and increases vagus nerve activity.
well as stimulation from vagosympathetic nerves, implies VNS then plays a multifaceted role in protecting the heart
that they receive signals from both sympathetic and through anti-inflammatory, alleviating mitochondrial
parasympathetic efferent axons, as well as sensory neurites dysfunction, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-remodeling
of the ventricle [16-19] . The intrinsic cardiac nervous system effects [24-28] (Figure 3). Electrically stimulating the
independently governs the cardiac function on a beat-by- parasympathetic nervous system using methods such
beat basis, even in the absence of external input from the as VNS, transcutaneous ear VNS (also known as tragus
central nervous system . The sinoatrial node is influenced stimulation, TS), ganglion plexus stimulation, and spinal
[14]
by both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous cord stimulation (SCS) enhances the activity of vagus
systems, which work in opposition to modulate heart nerves. The VNS device is frequently utilized in clinical
Figure 1. A model of the hierarchical control of the heart by the cardiac autonomic nervous system .
[10]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.0913