Page 33 - BH-1-2
P. 33
Brain & Heart Autonomic nerve and heart failure
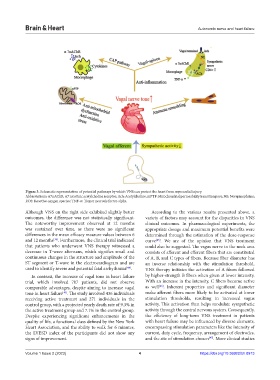
Figure 3. Schematic representation of potential pathways by which VNS can protect the heart from myocardial injury.
Abbreviations: α7nAChR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; Ach: Acetylcholine; mPTP: Mitochondrial permeability transition pore; NE: Norepinephrine;
ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Although VNS on the right side exhibited slightly better According to the various results presented above, a
outcomes, the difference was not statistically significant. variety of factors may account for the disparities in VNS
The noteworthy improvement observed at 12 months clinical outcomes. In pharmacological experiments, the
was sustained over time, as there were no significant appropriate dosage and maximum potential benefits were
differences in the mean efficacy measure values between 6 determined through the estimation of the dose-response
and 12 months . Furthermore, the clinical trial indicated curve . We are of the opinion that VNS treatment
[38]
[45]
that patients who underwent VNS therapy witnessed a could also be suggested. The vagus nerve in the neck area
decrease in T-wave alternans, which signifies small and consists of afferent and efferent fibers that are constituted
continuous changes in the structure and amplitude of the of A, B, and C types of fibers. Because fiber diameter has
ST segment or T-wave in the electrocardiogram and are an inverse relationship with the stimulation threshold,
used to identify severe and potential fatal arrhythmias . VNS therapy initiates the activation of A fibers followed
[44]
In contrast, the increase of vagal tone in heart failure by higher-strength B fibers when given at lower intensity.
trial, which involved 707 patients, did not observe With an increase in the intensity, C fibers become active
[46]
comparable advantages, despite aiming to increase vagal as well . Inherent properties and significant diameter
tone in heart failure . The study involved 436 individuals make afferent fibers more likely to be activated at lower
[40]
receiving active treatment and 271 individuals in the stimulation thresholds, resulting in increased vagus
control group, with a projected yearly death rate of 9.3% in activity. This activation then helps modulate sympathetic
the active treatment group and 7.1% in the control group. activity through the central nervous system. Consequently,
Despite experiencing significant enhancements in the the efficiency of long-term VNS treatment in patients
quality of life, a functional class defined by the New York with heart failure may be influenced by diverse elements,
Heart Association, and the ability to walk for 6 minutes, encompassing stimulation parameters like the intensity of
the LVESD index of the participants did not show any current, duty cycle, frequency, arrangement of electrodes,
signs of improvement. and the site of stimulation chosen . More clinical studies
[47]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.0913