Page 32 - BH-1-2
P. 32
Brain & Heart Autonomic nerve and heart failure
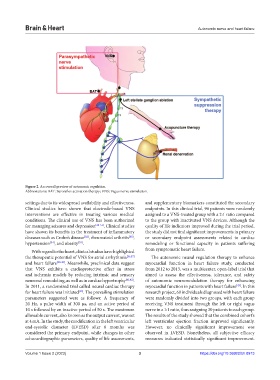
Figure 2. An overall preview of autonomic regulation.
Abbreviations: BAT: Baroreflex activation therapy; VNS: Vagus nerve stimulation.
settings due to its widespread availability and effectiveness. and supplementary biomarkers constituted the secondary
Clinical studies have shown that electrode-based VNS endpoints. In this clinical trial, 96 patients were randomly
interventions are effective in treating various medical assigned to a VNS-treated group with a 2:1 ratio compared
conditions. The clinical use of VNS has been authorized to the group with inactivated VNS devices. Although the
for managing seizures and depression [29-31] . Clinical studies quality of life indicators improved during the trial period,
have shown its benefits in the treatment of inflammatory the study did not find significant improvements in primary
diseases such as Crohn’s disease , rheumatoid arthritis , or secondary endpoint assessments related to cardiac
[32]
[33]
[34]
[35]
hypertension , and obesity . remodeling or functional capacity in patients suffering
With regard to the heart, clinical studies have highlighted from symptomatic heart failure.
the therapeutic potential of VNS for atrial arrhythmia [36,37] The autonomic neural regulation therapy to enhance
and heart failure [38-40] . Meanwhile, preclinical data suggest myocardial function in heart failure study, conducted
that VNS exhibits a cardioprotective effect in stress from 2012 to 2013, was a multicenter, open-label trial that
and ischemia models by reducing intrinsic and sensory aimed to assess the effectiveness, tolerance, and safety
neuronal remodeling, as well as in cardiac hypertrophy [41,42] . of autonomic neuromodulation therapy for enhancing
In 2011, a randomized trial called neural cardiac therapy myocardial function in patients with heart failure . In this
[43]
for heart failure was initiated . The prevailing stimulation research project, 60 individuals diagnosed with heart failure
[39]
parameters suggested were as follows: A frequency of were randomly divided into two groups, with each group
20 Hz, a pulse width of 300 μs, and an active period of receiving VNS treatment through the left or right vagus
10 s followed by an inactive period of 50 s. The maximum nerve in a 1:1 ratio, thus assigning 30 patients to each group.
allowable current, also known as the output current, was set The results of the study showed that the combined cohort’s
at 4 mA. In the study, the modification in the left ventricular left ventricular ejection fraction improved significantly.
end-systolic diameter (LVESD) after 6 months was However, no clinically significant improvement was
considered the primary endpoint, while changes in other observed in LVESD. Nonetheless, all subjective efficacy
echocardiographic parameters, quality of life assessments, measures indicated statistically significant improvement.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.0913