Page 35 - BH-1-2
P. 35
Brain & Heart Autonomic nerve and heart failure
research, whether the broader application of BAT in heart elevation in plasma catecholamine concentration, unlike
failure therapy is feasible. those with reduced ejection fraction . Compared to
[77]
other conventional therapeutic agents for heart failure,
4. Sympathetic suppression therapy such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)
4.1. Conventional pharmacological sympathetic and aldosterone antagonists, β-blockers tend to be more
suppression therapy efficacious in enhancing ejection fraction and possess
anti-ischemic properties that can lower the likelihood of
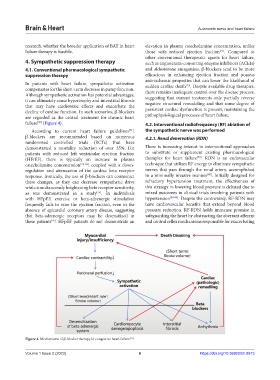
In patients with heart failure, sympathetic activation sudden cardiac death . Despite available drug therapies,
[73]
compensates for the short-term decrease in pump function. there remains inadequate control over the disease process,
Although sympathetic activation has potential advantages, suggesting that current treatments only partially reverse
it can ultimately cause hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis negative structural remodeling and that some degree of
that may have cardiotoxic effects and exacerbate the persistent cardiac dysfunction is present, maintaining the
decline of cardiac function. In such scenarios, β-blockers
are regarded as the central treatment for chronic heart pathophysiological processes of heart failure.
failure (Figure 4). 4.2. Interventional radiofrequency (RF) ablation of
[70]
According to current heart failure guidelines , the sympathetic nerve was performed
[71]
β-blockers are recommended based on numerous 4.2.1. Renal denervation (RDN)
randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that have
demonstrated a mortality reduction of over 35%. For There is increasing interest in interventional approaches
patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction to substitute or supplement existing pharmacological
[79]
(HFrEF), there is typically an increase in plasma therapies for heart failure . RDN is an endovascular
catecholamine concentration [72-74] , coupled with a down- technique that utilizes RF energy to eliminate sympathetic
regulation and attenuation of the cardiac beta receptor nerves that pass through the renal artery, accomplished
[80]
response. Ironically, the use of β-blockers can counteract in a minimally invasive manner . Initially designed for
these changes, as they can decrease sympathetic drive refractory hypertension treatment, the effectiveness of
while simultaneously heightening beta receptor sensitivity, this strategy in lowering blood pressure is debated due to
as was demonstrated in a study . In individuals mixed outcomes in clinical trials involving patients with
[75]
with HFpEF, exercise or beta-adrenergic stimulation hypertension [80-83] . Despite the controversy, RF-RDN may
frequently fails to raise the ejection fraction, even in the have cardiovascular benefits that extend beyond blood
absence of epicardial coronary artery disease, suggesting pressure reduction. RF-RDN holds immense promise in
that beta-adrenergic receptors may be desensitized in safeguarding the heart by obstructing the aberrant afferent
these patients . HFpEF patients do not demonstrate an and central reflex mechanisms responsible for exacerbating
[76]
Figure 4. Mechanisms of β-blocker therapy in congestive heart failure .
[75]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.0913