Page 29 - BH-2-2
P. 29
Brain & Heart Predictive modeling using electroencephalogram
relies on validation data to check how well various trained BCILAB and EEGLAB, which are MATLAB toolboxes.
models perform. Researchers are increasingly interested The proposed systematic approach includes:
in diving into more complex and automated feature (i) Signal processing is the process of taking unprocessed
extraction methods, suggesting that the field of feature data and transforming it into a form that can be read
extraction is reaching its point of diminishing returns. For and utilized by other devices.
certain biological signals, choosing the optimal feature (ii) Feature extraction can create the necessary feature
from extracted features may not always be straightforward vectors from either embedded or continuous signals.
since some features may not be equally informative, may (iii) Training and test data are fed into a predictive model.
lose some important information present in the raw data, (iv) The BCI paradigms standardize the full computational
23
or maybe noisy, correlated, or irrelevant. To understand approach, from data-driven model learning to offline
how to represent the data and make complex EEG data sets or real-time cognitive state prediction.
oscillatory data useful for categorization, ML models were (v) It is possible to connect certain pieces of hardware to
applied. the BCILAB’s data-crunching infrastructure by means
of online plug-ins and drivers.
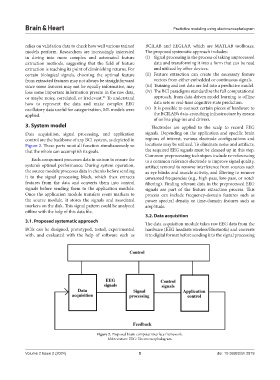
3. System model Electrodes are applied to the scalp to record EEG
Data acquisition, signal processing, and application signals. Depending on the application and specific brain
control are the backbone of any BCI system, as depicted in regions of interest, various electrode configurations and
Figure 2. These parts must all function simultaneously so locations may be utilized. To eliminate noise and artifacts,
that the whole can accomplish its goals. the acquired EEG signals must be cleaned up in this step.
Common preprocessing techniques include re-referencing
Each component processes data in unison to ensure the to a common reference electrode to improve signal quality,
system’s optimal performance. During system operation, artifact removal to remove interference from sources such
the source module processes data in chunks before sending as eye blinks and muscle activity, and filtering to remove
it to the signal processing block, which then extracts unwanted frequencies (e.g., high-pass, low-pass, or notch
features from the data and converts them into control filtering). Finding relevant data in the preprocessed EEG
signals before sending them to the application module. signals are part of the feature extraction process. This
Once the application module transfers event markers to process can include frequency-domain features such as
the source module, it stores the signals and associated power spectral density or time-domain features such as
markers on the disk. This signal pattern could be analyzed amplitude.
offline with the help of this data file.
3.2. Data acquisition
3.1. Proposed systematic approach
The data acquisition module takes raw EEG data from the
BCIs can be designed, prototyped, tested, experimented hardware (EEG headsets wireless/Bluetooth) and converts
with, and evaluated with the help of software such as it to digital format before sending it to the signal processing
Figure 2. Proposed brain-computer interface framework.
Abbreviation: EEG: Electroencephalogram.
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.2819