Page 65 - BH-2-4
P. 65
Brain & Heart Alzheimer’s disease: Gene and protein network analysis
A B
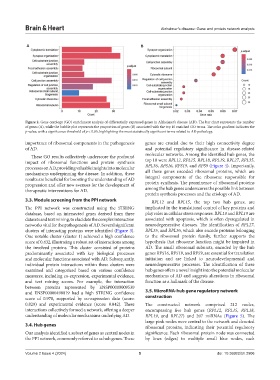
Figure 2. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The bar chart represents the number
of genes (A), while the bubble plot represents the proportion of genes (B) associated with the top 10 enriched GO terms. The color gradient indicates the
p-value, with a significance threshold of p < 0.05, highlighting the most statistically significant terms related to AD pathology.
importance of ribosomal components in the pathogenesis genes are crucial due to their high connectivity degree
of AD. and potential regulatory significance in disease-related
These GO results collectively underscore the profound molecular networks. Among the identified hub genes, the
impact of ribosomal functions and protein synthesis top 10 were RPL12, RPL15, RPL18, RPL19, RPL27, RPL35,
processes on AD, providing valuable insights into molecular RPL36, RPS16, RPS19, and RPS9 (Figure 4). Importantly,
mechanisms underpinning the disease. In addition, these all these genes encoded ribosomal proteins, which are
results are beneficial for boosting the understanding of AD integral components of the ribosome responsible for
progression and offer new avenues for the development of protein synthesis. The prominence of ribosomal proteins
therapeutic interventions for AD. among the hub genes underscores the possible link between
protein synthesis processes and the etiology of AD.
3.3. Module screening from the PPI network RPL12 and RPL15, the top two hub genes, are
The PPI network was constructed using the STRING implicated in the translational control of key proteins and
database, based on intersected genes derived from three play roles in cellular stress responses. RPL18 and RPL19 are
datasets and text mining, to elucidate the complex interaction associated with apoptosis, which is often dysregulated in
networks vital for the pathogenesis of AD. Several significant neurodegenerative diseases. The identification of RPL27,
clusters of interacting proteins were identified (Figure 3). RPL35, and RPL36, which also encode proteins belonging
One notable cluster (cluster 1) achieved a high confidence to the ribosomal protein family, further supports the
score of 0.432, illustrating a robust set of interactions among hypothesis that ribosome function might be impaired in
the involved proteins. This cluster consisted of proteins AD. The small ribosomal subunits, encoded by the hub
predominantly associated with key biological processes genes RPS16, RPS19, and RPS9, are essential for translation
and molecular functions associated with AD. Subsequently, initiation and are linked to neurodevelopmental and
individual protein interactions within these clusters were neurodegenerative processes. The identification of these
examined and categorized based on various confidence hub genes offers a novel insight into the potential molecular
measures, including co-expression, experimental evidence, mechanisms of AD and suggests alterations in ribosomal
and text mining scores. For example, the interaction function as a hallmark of the disease.
between proteins represented by ENSP00000009530
and ENSP00000498019 had a high STRING confidence 3.5. MicroRNA-hub gene regulatory network
score of 0.978, supported by co-expression data (score: construction
0.829) and experimental evidence (score: 0.842). These The constructed network comprised 212 nodes,
interactions collectively formed a network, offering a deeper encompassing five hub genes (RPL12, RPL15, RPL18,
understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying AD. RPL19, and RPL27) and 207 miRNAs (Figure 5). The
large pink nodes were central to the network and denoted
3.4. Hub genes ribosomal proteins, indicating their potential regulatory
Our analysis identified a subset of genes as central nodes in significance. Each ribosomal protein node was connected
the PPI network, commonly referred to as hub genes. These by lines (edges) to multiple small blue nodes, each
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.2906