Page 70 - BH-3-3
P. 70
Brain & Heart Dementia and the heart
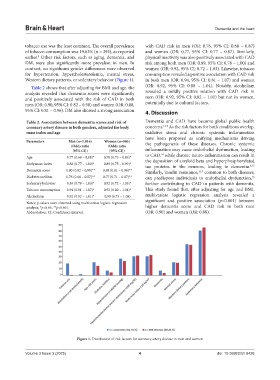
tobacco use was the least common. The overall prevalence with CAD risk in men (OR: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.68 – 0.87)
of tobacco consumption was 19.63% (n = 393), as reported and women (OR: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.77 – 0.87). Similarly,
earlier. Other risk factors, such as aging, dementia, and physical inactivity was also positively associated with CAD
9
DM, were also significantly more prevalent in men. In risk among both men (OR: 0.89, 95% CI: 0.78 – 1.00) and
contrast, no significant gender differences were observed women (OR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.72 – 1.03). Likewise, tobacco
for hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, mental stress, consumption revealed a positive association with CAD risk
Western dietary patterns, or sedentary behavior (Figure 1). in both men (OR: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.81 – 1.07) and women
Table 2 shows that after adjusting for BMI and age, the (OR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.80 – 1.04). Notably, alcoholism
analysis revealed that dementia scores were significantly revealed a mildly positive relation with CAD risk in
and positively associated with the risk of CAD in both men (OR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.82 – 1.01) but not in women,
men (OR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.82 – 0.98) and women (OR: 0.88, potentially due to cultural factors.
95% CI: 0.81 – 0.96). DM also showed a strong association 4. Discussion
Table 2. Association between dementia scores and risk of Dementia and CAD have become global public health
coronary artery disease in both genders, adjusted for body concerns. As the risk factors for both conditions overlap,
1,12
mass index and age oxidative stress and chronic systemic inflammation
have been proposed as unifying mechanisms driving
Parameters Men (n=1.016) Women (n=986) the pathogenesis of these diseases. Chronic systemic
(Odds ratio (Odds ratio
[95% CI]) [95% CI]) inflammation may cause endothelial dysfunction, leading
14
Age 0.77 (0.68 – 0.88)* 0.78 (0.73 – 0.89)* to CAD, while chronic neuro-inflammation can result in
the deposition of amyloid beta and hyperphosphorylated
Body mass index 0.88 (0.77 – 1.00)* 0.88 (0.75 – 0.99)* tau proteins in the neurons, leading to dementia.
8,15
Dementia score 0.90 (0.82 – 0.98)** 0.88 (0.81 – 0.96)** Similarly, insulin resistance, common to both diseases,
1,15
Diabetes mellitus 0.76 (0.68 – 0.87)** 0.77 (0.71 – 0.87)** can predispose individuals to endothelial dysfunction,
16
Sedentary behavior 0.89 (0.78 – 1.00)* 0.92 (0.72 – 1.03)* further contributing to CAD in patients with dementia.
Tobacco consumption 0.94 (0.81 – 1.07)* 0.92 (0.80 – 1.04)* This study found that, after adjusting for age and BMI,
Alcoholism 0.92 (0.82 – 1.01)* 0.90 (0.73 – 1.08) multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed a
Notes: p-values were obtained using multivariate logistic regression significant and positive association (p<0.001) between
analysis; *p<0.05, **p<0.001. higher dementia score and CAD risk in both men
Abbreviation: CI: Confidence interval. (OR: 0.90) and women (OR: 0.88).
Figure 1. Distribution of risk factors for coronary artery disease in men and women
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/bh.8426