Page 71 - BH-3-3
P. 71
Brain & Heart Dementia and the heart
While the exact pathogenesis of dementia remains deficiency and insulin resistance could be mediators of
unclear, chronic hypoperfusion and thrombosis are neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. While DM leads
considered key events in vascular dementia. These to brain insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and cognitive
conditions are associated with reduced cerebral blood impairment, its effects do not fully replicate the pathology
flow as well as increased levels of oxidative stress and of dementia. Disturbances in brain insulin and insulin-
inflammation. 16-18 These events, if they occur persistently, like growth factor signaling mechanisms contribute to
can damage the periventricular white matter, basal ganglia, the molecular, biochemical, and histopathological lesions
and hippocampus, impairing neurotransmission and observed in dementia. The term “type 3 DM” has been
neuro-synapsis. Vascular damage, such as atherosclerosis proposed to describe dementia, reflecting its unique
16
and cerebral amyloid angiopathy, in large and small vessels, features that resemble those of DM but specifically affect
such as the coronary artery, may predispose individuals the brain. 17,18 These brain lesions may be associated with a
with dementia to coronary thrombosis and myocardial decline in cognitive abilities, with insulin resistance acting
infarction, thus indicating that dementia could be an as a key mediator of neurodegeneration (Figure 2).
important risk factor for CAD and stroke. 15,16 Sedentary behavior was also significantly and positively
The amyloid cascade hypothesis proposes that the associated with CAD risk in both men (OR: 0.89) and
deposition of amyloid beta and hyperphosphorylated tau women (OR: 0.92). Likewise, tobacco consumption
in the brain plays a critical role in dementia. Additionally, demonstrated a positive association with CAD risk in men
there is evidence linking dementia with DM, as insulin (OR: 0.94) and women (OR: 0.92). Furthermore, alcoholism
resistance may contribute significantly to the development showed a modest positive association with CAD risk in
15
of dementia. Age-related brain insulin abnormalities are men (OR: 0.92) but not in women, potentially because
one of the causes of cognitive decline in mild cognitive most women do not consume alcohol. The association
impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. In the current study, of metabolic dysfunction, such as insulin resistance
DM was strongly associated with CAD risk in both men and homocysteinemia, with hormonal deficiencies may
(OR: 0.76) and women (OR: 0.77). contribute to various types of dementia, which in turn can
increase the risk of CAD. 1,19
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by increased
activation of pro-death genes, the accumulation of Among individuals above 64 years of age, the prevalence
neurofibrillary tangles, and dystrophic neurites and of dementia was significantly higher compared to the
signaling pathways, including impaired energy metabolism, younger age group (35.41% [n = 70] vs. 3.70% [n = 67]).
mitochondrial dysfunction, chronic oxidative stress, and The total prevalence of CAD was 11.40% (n = 230).
DNA damage. Recent evidence indicates that insulin There is evidence suggesting that DM may be associated
17
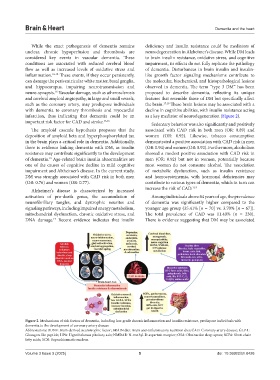
Figure 2. Mechanisms of risk factors of dementia, including low-grade chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, predispose individuals with
dementia to the development of coronary artery disease
Abbreviations: BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BRAIN diet: Brain anti-inflammatory nutrition diet; CAD: Coronary artery disease; GLP-1:
Glucagon like peptide; HPA: Hypothalamus pituitary axis; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; OSA: Obstructive sleep apnea; SCFA: Short chain
fatty acids; SCN: Suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/bh.8426