Page 32 - EER-2-2
P. 32
Explora: Environment
and Resource Anabaena-Azolla for crops and bioenergy
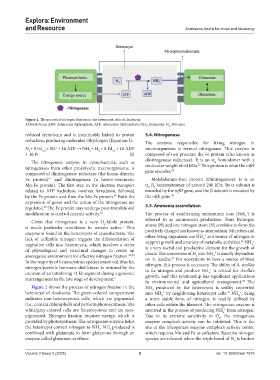
Figure 2. The process of nitrogen fixation in the heterocyst cells of Anabaena
Abbreviations: ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; NH : Ammonia; N : Nitrogen.
2
3
reduced ferredoxin and is inextricably linked to proton 5.4. Nitrogenase
reduction, producing molecular dihydrogen (Equation I): The enzyme responsible for fixing nitrogen in
N + 8 Fd + 8H + 16 ATP → NH + H + 8 Fd + 16 ADP microorganisms is termed nitrogenase. This enzyme is
+
2
ox
3
2
red
+ 16 Pi (I) composed of two proteins: the Fe protein (also known as
The nitrogenase enzyme in cyanobacteria, such as dinitrogenase reductase). It is an α homodimer with a
2
55
nitrogenases from other prokaryotic microorganisms, is molecular weight of 64 kDa. This protein is what the nifH
45
composed of dinitrogenase reductase (the homo-dimeric gene encodes.
Fe protein) and dinitrogenase (a hetero-tetrameric Molybdenum-Iron protein (Dinitrogenase): It is an
51
Mo-Fe protein). The first step in the electron transport α β heterotetramer of around 240 kDa. Its α subunit is
2
2
related to ATP hydrolysis involves ferredoxin, followed encoded by the nifD gene, and the β subunit is encoded by
by the Fe protein and then the Mo-Fe protein. Both the the nifK gene. 30
50
expression of genes and the action of the nitrogenase are
regulated. The Fe protein may undergo post-translational 5.5. Ammonia assimilation
52
+
modification to control enzyme activity. 51 The process of synthesizing ammonium ions (NH ) is
4
Given that nitrogenase is a very O -labile protein, referred to as ammonium production. Four hydrogen
2
it needs particular conditions to remain active. This atoms (H) and one nitrogen atom (N) combine to form the
1
enzyme is found in the heterocysts of cyanobacteria. The positively charged ion known as ammonium. Microbes and
+
lack of utilizable nitrogen triggers the differentiation of other living organisms use NH as a source of nitrogen to
4
56
+
vegetative cells into heterocysts, which involves a series support growth and a variety of metabolic activities. NH
4
of physiological and structural changes to create an is a very useful and productive element for the growth of
+
anoxygenic environment for effective nitrogen fixation. 53,54 plants. The conversion of N into NH is mostly dependent
2
4
on A. azollae. For ecosystems to have a source of fixed
57
In the majority of heterocystous species examined thus far, nitrogen, this process is necessary. The ability of A. azollae
nitrogen/juvenile hormone diol kinase is restored by the to fix nitrogen and produce NH is critical for Azolla’s
+
excision of an interfering 11 kb segment during a genomic growth, and this relationship has significant applications
4
rearrangement in the late stage of development. 1
in environmental and agricultural management. The
58
Figure 2 shows the process of nitrogen fixation in the NH produced by the heterocysts is swiftly converted
3
heterocyst of Anabaena. The green-colored compartment into NH by neighboring heterocyst cells. NH , being
+
59
+
4
4
indicates non-heterocystous cells, which are pigmented a more stable form of nitrogen, is readily utilized by
(i.e., contain chlorophyll) and perform photosynthesis. The other cells within the filament. The nitrogenase enzyme is
white/gray-colored cells are heterocystous and are non- involved in the process of producing NH from nitrogen.
+
4
pigmented. Nitrogen fixation requires energy, which is Due to its extreme sensitivity to O , the nitrogenase
2
provided by photosynthesis. The nitrogenase enzyme helps enzyme complex’s activity can be inhibited. This is the
the heterocyst convert nitrogen to NH . NH produced is site of the nitrogenase enzyme complex’s activity center,
3
3
combined with glutamate to form glutamine through an which requires Mo and Fe as cofactors. Reactive nitrogen
enzyme called glutamate synthase. species are released when the triple bond of N is broken
2
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/eer.7975