Page 40 - EER-2-2
P. 40
Explora: Environment
and Resource Anabaena-Azolla for crops and bioenergy
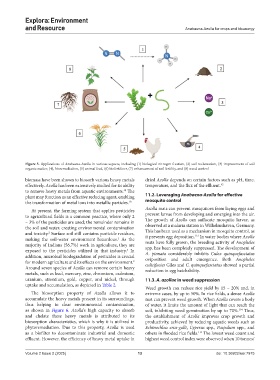
Figure 5. Applications of Anabaena-Azolla in various aspects, including (1) biological nitrogen fixation, (2) soil reclamation, (3) improvement of soil
organic matter, (4), bioremediation, (5) animal feed, (6) biofertilizer, (7) enhancement of soil fertility, and (8) weed control
biomass have been shown to biosorb various heavy metals dried Azolla depends on certain factors such as pH, time,
effectively. Azolla has been extensively studied for its ability temperature, and the flux of the effluent. 42
40
to remove heavy metals from aquatic environments. The
plant may function as an effective reducing agent, enabling 11.2. Leveraging Anabaena-Azolla for effective
the transformation of metal ions into metallic particles. 18 mosquito control
At present, the farming system that applies pesticides Azolla mats can prevent mosquitoes from laying eggs and
to agricultural fields is a common practice, where only 2 prevent larvae from developing and emerging into the air.
– 3% of the pesticides are used; the remainder remains in The growth of Azolla can suffocate mosquito larvae, as
the soil and water, creating environmental contamination observed at a malaria station in Wilhelmshaven, Germany.
and toxicity. Surface soil still contains pesticide residues, This has been used as a mechanism in mosquito control, as
2
it prevents egg deposition. In water bodies where Azolla
113
making the soil-water environment hazardous. As the mats have fully grown, the breeding activity of Anopheles
1
majority of Indians (56.7%) work in agriculture, they are spp. has been completely suppressed. The development of
exposed to the pesticides utilized in that industry. In A. pinnata considerably inhibits Culex quinquefasciatus
5
addition, microbial biodegradation of pesticides is crucial oviposition and adult emergence. Both Anopheles
for modern agriculture and its effects on the environment. culicifacies Giles and C. quinquefasciatus showed a partial
2
Around seven species of Azolla can remove certain heavy reduction in egg hatchability.
metals, such as lead, mercury, zinc, chromium, cadmium,
uranium, strontium, gold, copper, and nickel, through 11.3. A. azollae in weed suppression
uptake and accumulation, as depicted in Table 2.
Weed growth can reduce rice yield by 15 – 20% and, in
The biosorption property of Azolla allows it to extreme cases, by up to 50%. In rice fields, a dense Azolla
accumulate the heavy metals present in its surroundings, mat can prevent weed growth. When Azolla covers a body
thus helping to clear environmental contamination, of water, it limits the amount of light that can reach the
as shown in Figure 6. Azolla’s high capacity to absorb soil, inhibiting weed germination by up to 70%. Thus,
114
and chelate these heavy metals is attributed to its the establishment of Azolla improves crop growth and
biosorption characteristics, which is why it is utilized in productivity, achieved by reducing aquatic weeds such as
phytoremediation. Due to this property, Azolla is used Echinochloa crus-galli, Cyperus spp., Paspalum spp., and
as a biofilter to decontaminate industrial and domestic others in flooded rice fields. The lowest weed count and
114
effluent. However, the efficiency of heavy metal uptake in highest weed control index were observed when 10 tonnes/
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2025) 13 doi: 10.36922/eer.7975