Page 71 - EER-2-3
P. 71
Explora: Environment
and Resource ZnO and TiO nanoparticles and its impact on chickpeas
2
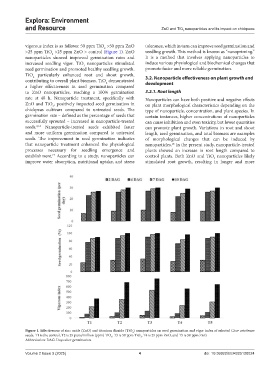
vigorous index is as follows: 50 ppm TiO >50 ppm ZnO tolerance, which in turn can improve seed germination and
2
>25 ppm TiO >25 ppm ZnO > control (Figure 1). ZnO seedling growth. This method is known as “nanopriming.”
2
nanoparticles showed improved germination rates and It is a method that involves applying nanoparticles to
increased seedling vigor. TiO nanoparticles stimulated induce various physiological and biochemical changes that
2
seed germination and promoted healthy seedling growth. promote faster and more reliable germination.
TiO particularly enhanced root and shoot growth,
2
contributing to overall plant biomass. TiO demonstrated 3.2. Nanoparticle effectiveness on plant growth and
development
2
a higher effectiveness in seed germination compared
to ZnO nanoparticles, reaching a 100% germination 3.2.1. Root length
rate at 48 h. Nanoparticle treatment, specifically with Nanoparticles can have both positive and negative effects
ZnO and TiO , positively impacted seed germination in on plant morphological characteristics depending on the
2
chickpeas cultivars compared to untreated seeds. The type of nanoparticle, concentration, and plant species. In
germination rate – defined as the percentage of seeds that certain instances, higher concentrations of nanoparticles
successfully sprouted – increased in nanoparticle-treated can cause inhibition and even toxicity, but lower quantities
seeds. Nanoparticle-treated seeds exhibited faster can promote plant growth. Variations in root and shoot
4,16
and more uniform germination compared to untreated length, seed germination, and total biomass are examples
seeds. The improvement in seed germination indicates of morphological changes that can be induced by
that nanoparticle treatment enhanced the physiological nanoparticles. In the present study, nanoparticle-treated
18
processes necessary for seedling emergence and plants showed an increase in root length compared to
establishment. According to a study, nanoparticles can control plants. Both ZnO and TiO nanoparticles likely
17
2
improve water absorption, nutritional uptake, and stress stimulated root growth, resulting in longer and more
Figure 1. Effectiveness of zinc oxide (ZnO) and titanium dioxide (TiO ) nanoparticles on seed germination and vigor index of selected Cicer arietinum
2
seeds. T1 is the control, T2 is 25 parts/million (ppm) TiO , T3 is 50 ppm TiO , T4 is 25 ppm ZnO, and T5 is 50 ppm ZnO.
2
2
Abbreviation: DAG: Days after germination.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/EER025120024