Page 75 - EER-2-3
P. 75
Explora: Environment
and Resource ZnO and TiO nanoparticles and its impact on chickpeas
2
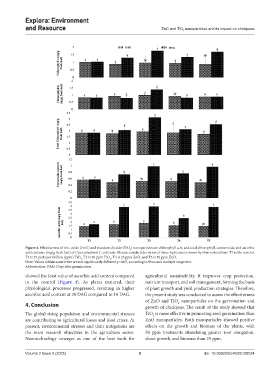
Figure 4. Effectiveness of zinc oxide (ZnO) and titanium dioxide (TiO ) nanoparticles on chlorophyll a, b, and total chlorophyll, carotenoids, and ascorbic
2
acid contents (mg/g fresh leaf) of Cicer arietinum L. cultivars. Mean± standard deviation of three replicates is shown by thin vertical bars. T1 is the control,
T2 is 25 parts per million (ppm) TiO , T3 is 50 ppm TiO , T4 is 25 ppm ZnO, and T5 is 50 ppm ZnO.
2
2
Note: Values within same letter are not significantly different p<0.05, according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
Abbreviation: DAG: Days after germination.
showed the least value of ascorbic acid content compared agricultural sustainability. It improves crop protection,
to the control (Figure 4). As plants matured, their nutrient transport, and soil management, forming the basis
physiological processes progressed, resulting in higher of plant growth and yield production strategies. Therefore,
ascorbic acid content at 20 DAG compared to 10 DAG. the present study was conducted to assess the effectiveness
of ZnO and TiO nanoparticles on the germination and
4. Conclusion growth of chickpeas. The result of the study showed that
2
The global rising population and environmental stresses TiO is more effective in promoting seed germination than
2
are contributing to agricultural losses and food crises. At ZnO nanoparticles. Both nanoparticles showed positive
present, environmental stresses and their mitigations are effects on the growth and biomass of the plants, with
the main research objectives in the agriculture sector. 50 ppm treatments stimulating greater root elongation,
Nanotechnology emerges as one of the best tools for shoot growth, and biomass than 25 ppm.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/EER025120024