Page 73 - EER-2-3
P. 73
Explora: Environment
and Resource ZnO and TiO nanoparticles and its impact on chickpeas
2
in plant cells. To increase crop yields, nanoparticles treated C. arietinum L. cultivars exhibited higher fresh
are often used as nanofertilizers, nanoinsecticides, and weight compared to untreated plants. The increase in fresh
nanofungicides. Various nanoparticles, such as TiO , ZnO, weight indicates greater water content and overall biomass
2
silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, gold, and silver, are being accumulation in nanoparticle-treated plants. Enhanced
used to improve soil fertility, manage nutrients, and boost fresh weight suggests improved growth and physiological
crop yields. 4 activity in response to nanoparticle treatments.
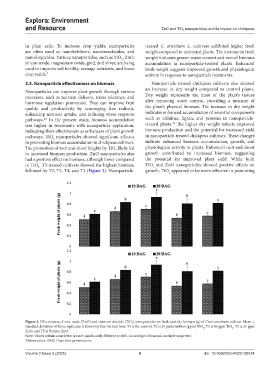
3.3. Nanoparticle effectiveness on biomass Nanoparticle-treated chickpeas cultivars also showed
an increase in dry weight compared to control plants.
Nanoparticles can improve plant growth through various
processes, such as nutrient delivery, stress tolerance, and Dry weight represents the mass of the plant’s tissues
hormone regulation promotion. They can improve fruit after removing water content, providing a measure of
quality and productivity by scavenging free radicals, the plant’s physical biomass. The increase in dry weight
enhancing nutrient uptake, and inducing stress response indicates enhanced accumulation of essential components
pathways. In the present study, biomass accumulation such as cellulose, lignin, and proteins in nanoparticle-
4,9
19
was higher in treatments with nanoparticle application, treated plants. The higher dry weight reflects improved
indicating their effectiveness as enhancers of plant growth biomass production and the potential for increased yield
pathways. TiO nanoparticles showed significant efficacy in nanoparticle-treated chickpeas cultivars. These changes
2
in promoting biomass accumulation in chickpeas cultivars. indicate enhanced biomass accumulation, growth, and
The promotion of root and shoot heights by TiO likely led physiological activity in plants. Enhanced root and shoot
2
to increased biomass production. ZnO nanoparticles also growth contributed to increased biomass, suggesting
had a positive effect on biomass, although lower compared the potential for improved plant yield. While both
to TiO . T3-treated cultivars showed the highest biomass, TiO and ZnO nanoparticles showed positive effects on
2
2
followed by T2, T5, T4, and T1 (Figure 3). Nanoparticle- growth, TiO appeared to be more effective in promoting
2
Figure 3. Effectiveness of zinc oxide (ZnO) and titanium dioxide (TiO ) nanoparticles on fresh and dry biomass (g) of Cicer arietinum cultivar. Mean ±
2
standard deviation of three replicates is shown by thin vertical bars. T1 is the control, T2 is 25 parts/million (ppm) TiO , T3 is 50 ppm TiO , T4 is 25 ppm
2
2
ZnO, and T5 is 50 ppm ZnO.
Note: Values within same letter are not significantly different p<0.05, according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
Abbreviation: DAG: Days after germination.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/EER025120024