Page 162 - EJMO-9-1
P. 162
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
Potential of flavonoids against glioblastoma
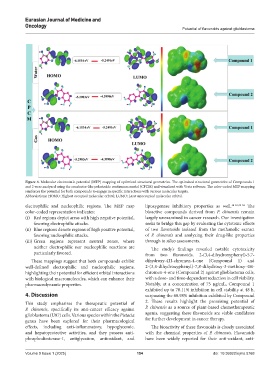
Figure 4. Molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) mapping of optimized structural geometries. The optimized structural geometries of Compounds 1
and 2 were analyzed using the conductor-like polarizable continuum model (CPCM) and visualized with Vesta software. The color-coded MEP mapping
reinforces the potential for both compounds to engage in specific interactions with various molecular targets.
Abbreviations: HOMO: Highest occupied molecular orbital; LUMO: Least unoccupied molecular orbital.
electrophilic and nucleophilic regions. The MEP map lipoxygenase inhibitory properties as well. 14-16,32-34 The
color-coded representation indicates: bioactive compounds derived from P. chinensis remain
(i) Red regions depict areas with high negative potential, largely unexamined in cancer research. Our investigation
favoring electrophilic attacks. seeks to bridge this gap by evaluating the cytotoxic effects
(ii) Blue regions denote regions of high positive potential, of two flavonoids isolated from the methanolic extract
favoring nucleophilic attacks. of P. chinensis and analyzing their drug-like properties
(iii) Green regions represent neutral zones, where through in silico assessments.
neither electrophilic nor nucleophilic reactions are The study’s findings revealed notable cytotoxicity
particularly favored. from two flavonoids, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-
These mappings suggest that both compounds exhibit dihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one (Compound 1) and
well-defined electrophilic and nucleophilic regions, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7,8-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-4H-
highlighting their potential for efficient orbital interactions chromen-4-one (Compound 2) against glioblastoma cells,
with biological macromolecules, which can enhance their with a dose- and time-dependent reduction in cell viability.
pharmacodynamic properties. Notably, at a concentration of 75 µg/mL, Compound 1
exhibited up to 70.11% inhibition in cell viability at 48 h,
4. Discussion surpassing the 68.98% inhibition exhibited by Compound
This study emphasizes the therapeutic potential of 2. These results highlight the promising potential of
P. chinensis, specifically its anti-cancer efficacy against P. chinensis as a source of plant-based chemotherapeutic
glioblastoma (U87) cells. Various species within the Pistacia agents, suggesting these flavonoids are viable candidates
genus have been explored for their pharmacological for further development in cancer therapy.
effects, including anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, The bioactivity of these flavonoids is closely associated
and hepatoprotective activities, and they possess anti- with the chemical properties of P. chinensis. Flavonoids
phosphodiesterase-1, antiglycation, antioxidant, and have been widely reported for their anti-oxidant, anti-
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 154 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.5768