Page 273 - EJMO-9-2
P. 273
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology ANGPTL8 upregulation in CRC with liver metastasis
A B
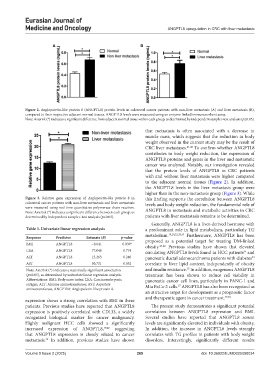
Figure 2. Angiopoietin-like protein 8 (ANGPTL8) protein levels in colorectal cancer patients with non-liver metastasis (A) and liver metastasis (B),
compared to their respective adjacent normal tissues. ANGPTL8 levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Note: Asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference from adjacent normal tissue within each group, as determined by independent sample t-test analysis (p≤0.05).
that metastasis is often associated with a decrease in
muscle mass, which suggests that the reduction in body
weight observed in the current study may be the result of
CRC liver metastases. 41,42 To confirm whether ANGPTL8
contributes to body weight reduction, the expression of
ANGPTL8 proteins and genes in the liver and metastatic
cancer was analyzed. Notably, our investigation revealed
that the protein levels of ANGPTL8 in CRC patients
with and without liver metastasis were higher compared
to the adjacent normal tissues (Figure 2). In addition,
the ANGPTL8 levels in the liver metastasis group were
higher than in the non-metastasis group (Figure 3). While
Figure 3. Relative gene expression of Angiopoietin-like protein 8 in this finding supports the correlation between ANGPTL8
colorectal cancer patients with non-liver metastasis and liver metastasis levels and body weight reduction, the fundamental role of
were measured using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. ANGPTL8 in metastasis and metabolic activities in CRC
Note: Asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference between each group, as
determined by independent sample t-test analysis (p≤0.05). patients with liver metastasis remains to be determined.
Generally, ANGPTL8 is a liver-derived hormone with
Table 3. Univariate linear regression analysis a predominant role in lipid metabolism, particularly TG
Response Predictor Estimate (B) p-value metabolism. 19,20,22,29,43 Furthermore, ANGPTL8 has been
BMI ANGPTL8 −8.641 0.039* proposed as a potential target for treating DM-linked
Previous studies have shown that elevated
obesity.
43-46
CEA ANGPTL8 77.048 0.774 circulating ANGPTL8 levels found in HCC patients and
34
ALT ANGPTL8 15.263 0.240 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients with diabetes
44
AST ANGPTL8 50.731 0.052 correlate to liver lipid content, independently of obesity
35
Note: Asterisk (*) indicates a statistically significant association and insulin resistance. In addition, exogenous ANGPTL8
(p≤0.05), as determined by univariate linear regression analysis. treatment has been shown to reduce cell viability in
Abbreviations: BMI: Body mass index; CEA: Carcinoembryonic pancreatic cancer cell lines, particularly in PANC-1 and
antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate Mia PaCa-2 cells. ANGPTL8 has also been recognized as
37
aminotransferase, ANGPTL8: Angiopoietin-like protein 8.
an attractive target for development as a prognostic factor
and therapeutic agent in cancer treatment. 47,48
expression shows a strong correlation with BMI in these
patients. Previous studies have reported that ANGPTL8 The present study demonstrates a significant potential
expression is positively correlated with CD133, a widely correlation between ANGPTL8 expression and BMI.
recognized biological marker for cancer malignancy. Several studies have reported that ANGPTL8 serum
Highly malignant HCC cells showed a significantly levels are significantly elevated in individuals with obesity.
increased expression of ANGPTL8, 39,40 suggesting In addition, the increase in ANGPTL8 levels strongly
that ANGPTL8 expression is closely related to cancer correlates with TG profiles in patients with body weight
metastasis. In addition, previous studies have shown disorders. Interestingly, significantly different results
39
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 265 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025080034