Page 52 - ESAM-1-2
P. 52
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing Multi-material additive manufacturing of metals
A
B
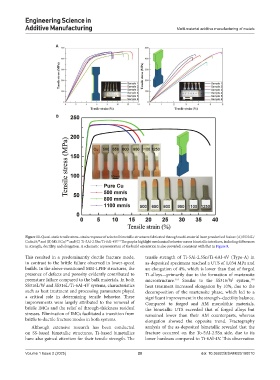
Figure 11. Quasi-static tensile stress–strain response of selected bimetallic structures fabricated throughmulti-material laser powder bed fusion: (A) SS316L/
CuSn10; and (B) MS1/Cu; and (C) Ti-5Al-2.5Sn/Ti-6Al-4V. The graphs highlight mechanical behavior across bimetallic interfaces, including differences
179
58
151
in strength, ductility, and elongation. A schematic representation of the build orientation is also provided, consistent with that in Figure 9.
This resulted in a predominantly ductile fracture mode, tensile strength of Ti-5Al-2.5Sn/Ti-6Al-4V (Type-A) in
in contrast to the brittle failure observed in lower-speed as-deposited specimens reached a UTS of 1,034 MPa and
builds. In the above-mentioned MM-LPBF structures, the an elongation of 4%, which is lower than that of forged
presence of defects and porosity evidently contributed to Ti-alloys—primarily due to the formation of martensite
premature failure compared to the bulk materials. In both microstructure. Similar to the SS316/W system,
151
148
SS316L/W and SS316L/Ti-6Al-4V systems, characteristics heat treatment increased elongation by 10%, due to the
such as heat treatment and processing parameters played decomposition of the martensite phase, which led to a
a critical role in determining tensile behavior. These significant improvement in the strength–ductility balance.
improvements were largely attributed to the removal of Compared to forged and AM monolithic materials,
brittle IMCs and the relief of through-thickness residual the bimetallic UTS exceeded that of forged alloys but
stresses. Elimination of IMCs facilitated a transition from remained lower than their AM counterparts, whereas
brittle to ductile fracture modes in both systems. elongation showed the opposite trend. Fractography
Although extensive research has been conducted analysis of the as-deposited bimetallic revealed that the
on SS-based bimetallic structures, Ti-based bimetallics fracture occurred on the To-5Al-2.5Sn side, due to its
have also gained attention for their tensile strength. The lower hardness compared to Ti-6Al-4V. This observation
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 20 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025180010