Page 27 - ESAM-1-4
P. 27
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing Machine learning for biomedical metal AM
frequently challenging to acquire due to concerns regarding predict unknown data. Supervised learning is further
commercial sensitivity. 41,42 To address fundamental divided into regression and classification. Regression
challenges such as data scarcity, heterogeneity, and primarily handles continuous variables, while
insufficient high-quality labeled data, researchers employ classification deals with discrete variables. Regression
diverse strategies, including multimodal data fusion algorithms encompass a range of methods, including
and transfer learning. Subsequent preprocessing steps, linear regression, Gaussian process regression (GPR),
including data sampling, anomaly detection and handling, and regression trees. The applications of regression
data discretization, and standardization, have been shown algorithms in the field of AM primarily encompass
to enhance training efficiency and prediction accuracy. the following: process window prediction, process
The objective of feature engineering is to extract or parameter optimization, alloy property prediction,
construct features that are most representative of the geometric deviation control, and closed-loop
prediction target from raw data, thus serving as a key factor control. Common classification algorithms include
in enhancing model performance. Common methods linear discriminant analysis, naïve Bayes, support
include principal component analysis, independent vector machines (SVM), K-nearest neighbors,
component analysis, categorical encoding, and clustering. random forest, and classification trees. 48,49 The
The process of feature engineering has been shown to primary applications of these algorithms encompass
reduce dimensionality, thereby eliminating redundancy defect detection, quality assessment, and geometric
and highlighting key parameters that influence material deviation control.
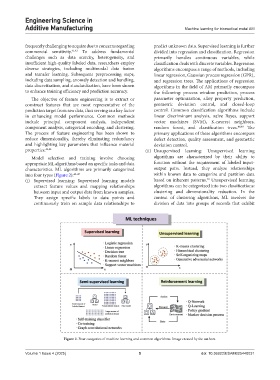
properties. 43,44 (ii) Unsupervised learning: Unsupervised learning
Model selection and training involve choosing algorithms are characterized by their ability to
appropriate ML algorithms based on specific tasks and data function without the requirement of labeled input-
characteristics. ML algorithms are primarily categorized output pairs. Instead, they analyze relationships
into four types (Figure 2): 45-47 within known data to categorize and partition data
(i) Supervised learning: Supervised learning models based on inherent patterns. Unsupervised learning
50
extract feature values and mapping relationships algorithms can be categorized into two classifications:
between input and output data from known samples. clustering and dimensionality reduction. In the
They assign specific labels to data points and context of clustering algorithms, ML involves the
continuously train on sample data relationships to division of data into groups of records that exhibit
Figure 2. Four categories of machine learning and common algorithms. Image created by the authors.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025440031