Page 29 - ESAM-1-4
P. 29
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing Machine learning for biomedical metal AM
ML, for enhancing quality assurance and advancing 2. ML-driven forward prediction of AM
intelligent manufacturing in AM. Inayathullah et al. biomedical metals
62
focused on physics-aware hybrid data approaches and
evaluated the performance of various advanced ML 2.1. Overview
algorithms in enhancing the precision and efficiency Forward prediction in AM refers to the use of ML models to
of AM. This review, therefore, narrows its scope to the forecast the performance metrics of final products based on
specific domain of ML applications in AM process of known process parameters, material composition, or initial
biomedical metals. conditions. This approach follows the process-structure–
58
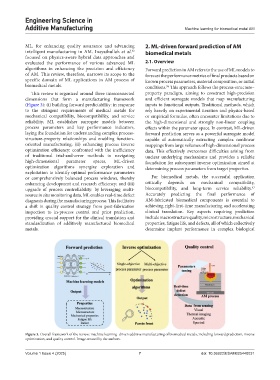
This review is organized around three interconnected property paradigm, aiming to construct high-precision
dimensions that form a manufacturing framework and efficient surrogate models that map manufacturing
(Figure 3): (i) building forward predictability: in response inputs to functional outputs. Traditional methods, which
to the stringent requirements of medical metals for rely heavily on experimental iteration and physics-based
mechanical compatibility, biocompatibility, and service or empirical formulas, often encounter limitations due to
reliability, ML establishes surrogate models between the high-dimensional and strongly non-linear coupling
process parameters and key performance indicators, effects within the parameter space. In contrast, ML-driven
laying the foundation for understanding complex process- forward prediction serves as a powerful surrogate model
structure-property relationships and enabling function- capable of automatically extracting complex nonlinear
oriented manufacturing; (ii) enhancing process inverse mappings from large volumes of high-dimensional process
optimization efficiency: confronted with the inefficiency data. This effectively overcomes difficulties arising from
of traditional trial-and-error methods in navigating unclear underlying mechanisms and provides a reliable
high-dimensional parameter spaces, ML-driven foundation for subsequent inverse optimization aimed at
optimization algorithms synergize exploration and determining process parameters from target properties.
exploitation to identify optimal performance parameters
or comprehensively balanced process windows, thereby For biomedical metals, the successful application
enhancing development and research efficiency; and (iii) critically depends on mechanical compatibility,
63
upgrade of process controllability: by leveraging multi- biocompatibility, and long-term service reliability.
source in situ monitoring data, ML enables real-time defect Accurately predicting the final performance of
diagnosis during the manufacturing process. This facilitates AM-fabricated biomedical components is essential to
a shift in quality control strategy from post-fabrication achieving right-first-time manufacturing and accelerating
inspection to in-process control and prior prediction, clinical translation. Key aspects requiring prediction
providing crucial support for the clinical translation and include macrostructure quality, microstructure, mechanical
standardization of additively manufactured biomedical properties, fatigue life, and defects, all of which collectively
metals. determine implant performance in complex biological
Figure 3. Overall framework of the review: machine learning–driven additive manufacturing of biomedical metals, including forward prediction, inverse
optimization, and quality control. Image created by the authors.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025440031