Page 91 - GHES-1-2
P. 91
Global Health Econ Sustain Non-communicable diseases household survey
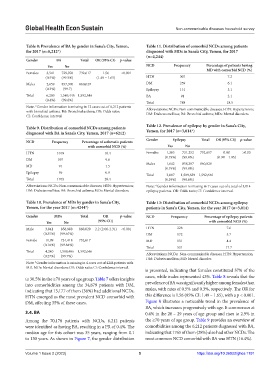
Table 8: Prevalence of BA by gender in Sana’a City, Yemen, Table 11. Distribution of comorbid NCDs among patients
for 2017 (n=6,212*) diagnosed with MDs in Sana’a City, Yemen, for 2017
(n=4,244)
Gender BA Total OR (95% CI) p‑value
Yes No NCD Frequency Percentage of patients having
MD with comorbid NCD (%)
Females 3,541 729,076 732,617 1.56 <0.001
(0.5%) (99.5%) (1.49 – 1.65) HTN 307 7.2
Males 2,659 857,370 860,029 DM 259 6.1
(0.3%) (99.7) Epilepsy 131 3.1
Total 6,200 1,586,446 1,592,646 BA 91 2.1
(0.4%) (99.6%)
Total 788 18.5
Note: *Gender information is missing in 12 cases out of 6,212 patients
with bronchial asthma. BA: Bronchial asthma; OR: Odds ratio; Abbreviations: NCDs: Non-communicable diseases; HTN: Hypertension;
CI: Confidence interval. DM: Diabetes mellitus; BA: Bronchial asthma; MDs: Mental disorders.
Table 12. Prevalence of epilepsy by gender in Sana’a City,
Table 9. Distribution of comorbid NCDs among patients
diagnosed with BA in Sana’a City, Yemen, 2017 (n=6212) Yemen, for 2017 (n=3,014*)
Gender Epilepsy Total OR (95% CI)) p‑value
NCD Frequency Percentage of asthmatic patients
with comorbid NCD (%) Yes No
HTN 1018 16.4 Females 1,365 731,252 732,617 0.98 >0.05
(0.19%) (99.8%) (0.90 – 1.05)
DM 597 9.6
Males 1,642 858,387 860,029
MD 91 1.5 (0.19%) (99.8%)
Epilepsy 59 0.9
Total 3,007 1,589,639 1,592,646
Total 1765 28.4 (0.19%) (99.8%)
Abbreviations: NCDs: Non-communicable diseases; HTN: Hypertension; Note: *Gender information is missing in 7 cases out of a total of 3,014
DM: Diabetes mellitus; BA: Bronchial asthma; MDs: Mental disorders. epilepsy patients. OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
Table 10. Prevalence of MDs by gender in Sana’a City, Table 13: Distribution of comorbid NCDs among epilepsy
Yemen, for the year 2017 (n=4244*) patients in Sana’a City, Yemen, for the year 2017 (n=3,014)
Gender MDs Total OR p‑value NCD Frequency Percentage of epilepsy patients
Yes No (95% CI)) with comorbid NCD (%)
Male 3,041 856,988 860,029 2.2 (2.06-2.31) <0.001 HTN 228 7.6
(0.35%) (99.65%) DM 172 5.7
Female 11,99 731,418 732,617 MD 131 4.4
(0.16%) (99.84%)
Total 531 17.7
Total 4,240 1,588,406 1,592,646
(0.27%) (99.7%) Abbreviations: NCDs: Non-communicable diseases; HTN: Hypertension;
DM: Diabetes mellitus; MD: Mental disorder.
Note: *Gender information is missing in 4 cases out of 4244 patients with
MD. MDs: Mental disorders; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
is presented, indicating that females constituted 57% of the
to 30.5% in the ≥70 years of age group. Table 7 offers insights cases, while males represented 43%. Table 8 reveals that the
into comorbidities among the 34,879 patients with DM, prevalence of BA was significantly higher among females than
indicating that 13,177 of them (38%) had additional NCDs. males, with rates of 0.5% and 0.3%, respectively. The OR for
HTN emerged as the most prevalent NCD comorbid with this difference is 1.56 (95% CI: 1.49 – 1.65), with a p < 0.001.
DM, affecting 35% of these cases. Figure 8 illustrates a noticeable trend in the prevalence of
BA, which increases progressively with age. It commences at
3.4. BA 0.4% in the 20 – 29 years of age group and rises to 2.9% in
Among the 70,178 patients with NCDs, 6,212 patients the ≥70 years of age group. Table 9 provides an overview of
were identified as having BA, resulting in a PR of 0.4%. The comorbidities among the 6,212 patients diagnosed with BA,
median age for this cohort was 35 years, ranging from 0.1 indicating that 1765 of them (28%) also had other NCDs. The
to 130 years. As shown in Figure 7, the gender distribution most common NCD comorbid with BA was HTN (16.4%).
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1191